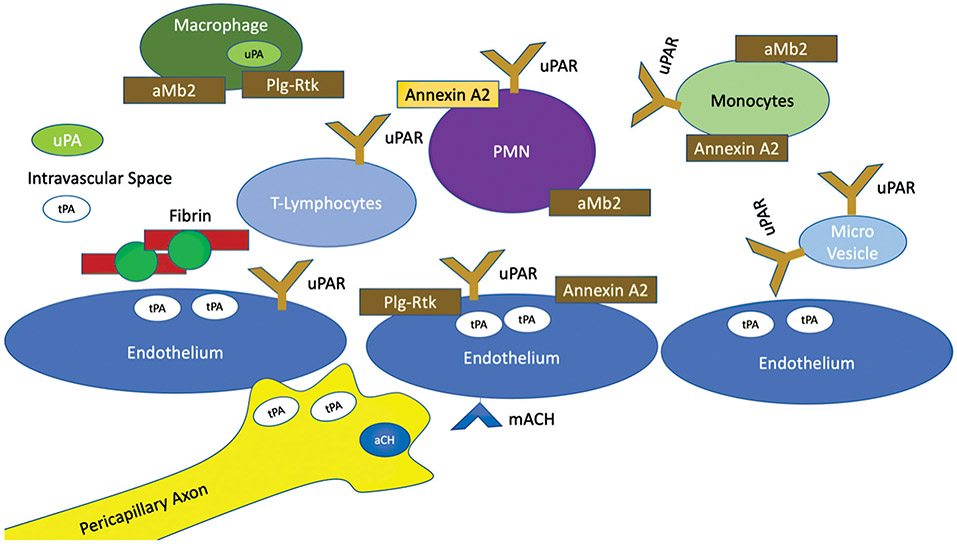
Fig. 1.
Cellular mediators of fibrinolysis activation. This figure demonstrates a schematic on the numerous potential cellular regulators of fibrinolysis. Basal levels of plasminogen activators (tPA and uPA) are present in the systemic circulation. There are additional cellular factors that can release tPA and uPA based on stimuli, in addition to neurons that can directly release tPA and also release neurotransmitters for local tPA release. Many circulating cells also have receptors for plasminogen and uPA which further help localize plasminogen activators in proximity to plasminogen. With local fibrin production, additional binding of plasminogen can occur which also enables tPA binding, enabling high concentrations of cellular and non–cellular-mediated fibrinolysis. tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; uPAR, urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor.