Figure 2: sRNA Synthesis.
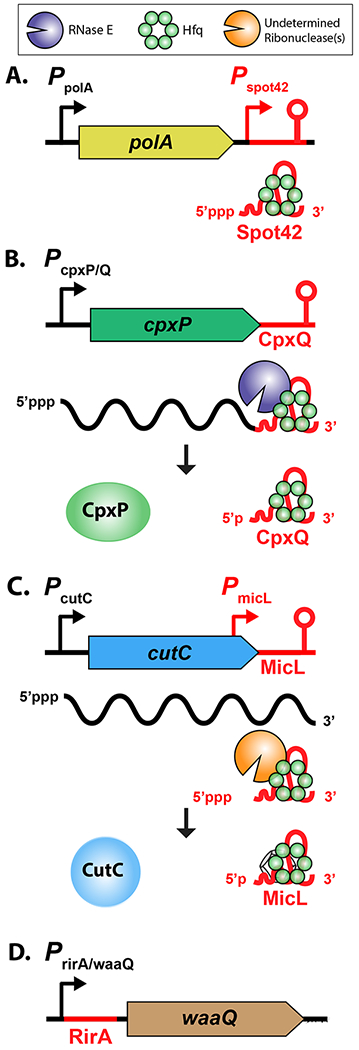
A. Many sRNAs are transcribed from intergenic regions as free-standing transcripts [11] [12] (Spot 42, reviewed in [55], is shown as an example); their abundance in the cell is primarily regulated at the level of transcription, and this is frequently highly regulated.
B. sRNAs can also be synthesized from processing of mRNAs (as for CpxP; [19]); in this case, regulatory signals for the mRNA promoter will also govern synthesis of the sRNA.
C. sRNA promoters may also be embedded within mRNA coding regions (as for MicL here; [18]). In this case, regulation of the upstream gene can be independent of transcription of the overlapping mRNA. The promoter for MicL is a sigma E-dependent promoter [18]; further processing takes place to create the final sRNA.
D. Evidence has also accumulated for sRNAs arising from the 5’ UTR of mRNAs [15]. In the case shown, it is not clear that RirA is an Hfq-dependent sRNA (RirA) [20].
