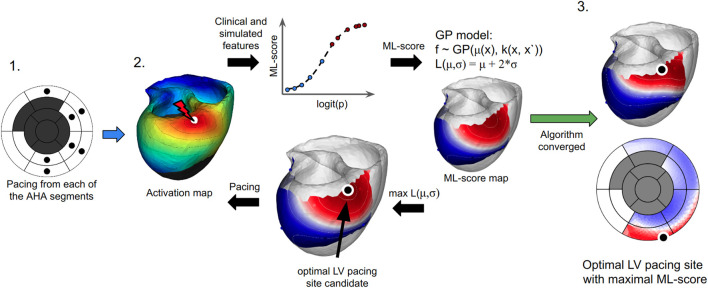
FIGURE 2.
The algorithm for finding the optimal LV pacing site involves three major steps: (1) To compute ventricular activation maps (color map shows activation times of the ventricular regions with early activated regions shown in red and late activated areas shown in blue) from the personalized model at BiV pacing with LV pacing site (white dot) located at every centre of the AHA LV model (excluding the septal and postinfarction scar segments marked as dark gray on the left panel). (2) To apply an LR classifier of CRT response and iterative Bayesian optimization procedure with Gaussian process regression to predict ML-scores on the LV surface. Model-derived features and patient clinical data for each LV pacing site are fed to an LR classifier (shown schematically as a graph in the middle top. The plot shows the LR function calculated for each LV pacing site tested. The x-axis shows a linear combination of the input features (logit(p)) used to calculate the LR value (ML-score). Red and blue dots show positive (red) and negative (blue) predictions of CRT response based on ML-score > <0.51). The LR classifier generates an initial array of ML-scores for interpolation. A Gaussian process regression model is then trained to estimate the GP acquisition function L (mu,sigma) and predict ML-score values on the entire LV surface (see two color maps on the LV surface with shades of red for ML-score > 0.5 and shades of blue for ML-score < 0.5). The target point candidate is found by approaching the maximum value of the acquisition function (black dot). A new ventricular activation map and simulated features are computed at BiV pacing with the LV site located at the current candidate point. The simulated features in the next iteration step are fed again to the LR classifier to generate an ML-score and retrain the GP regression with accounting for this value or further interpolation of ML-score on the LV surface. (3) The algorithm converges if two iterations predict the same candidate point. The last point with the maximum ML-score value provides an optimal LV pacing site (black dot). The resulting ML-score map is displayed on the LV surface of the personalized LV model and the LV AHA segment scheme.