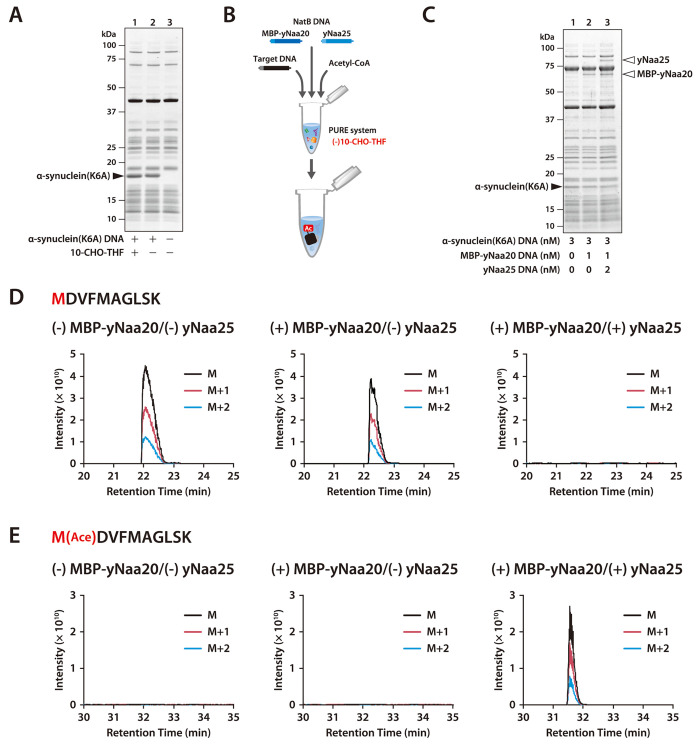
Figure 1.
NatB-mediated N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein(K6A). (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of α-synuclein(K6A) synthesized in the presence or absence of 10-formyl tetrahydrofolate (10-CHO-THF) at 37 °C for 4 h. (B) Schematic outline of NatB-mediated N-terminal acetylation. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of α-synuclein(K6A) cosynthesized with MBP-yNaa20 and yNaa25. α-Synuclein(K6A) DNA (3 nM), MBP-yNaa20 DNA (1 nM), and yNaa25 DNA (2 nM) were added to the PURE system ((−) 10-CHO-THF) containing 5 μM DnaK, 1 μM DnaJ, 1 μM GrpE, and 1 mM acetyl-CoA, as indicated. The reaction mixture was incubated at 23 °C for 24 h. (D) Extracted ion chromatograms of the unmodified N-terminal peptide derived from α-synuclein(K6A) after trypsin digestion (MDVFMAGLSK, M = 549.7697 Da, M+1 = 550.2712 Da, M+2 = 550.7710 Da, z = 2). The retention time was confirmed by the peptide search results from the MS/MS spectral search. (E) Extracted ion chromatograms of the acetylated N-terminal peptide derived from α-synuclein(K6A) after trypsin digestion (M[Ace]-DVFMAGLSK, M = 570.7750 Da, M+1 = 571.2765 Da, M+2 = 571.7764 Da, z = 2). The retention time was confirmed by the peptide search results from the MS/MS spectral search.