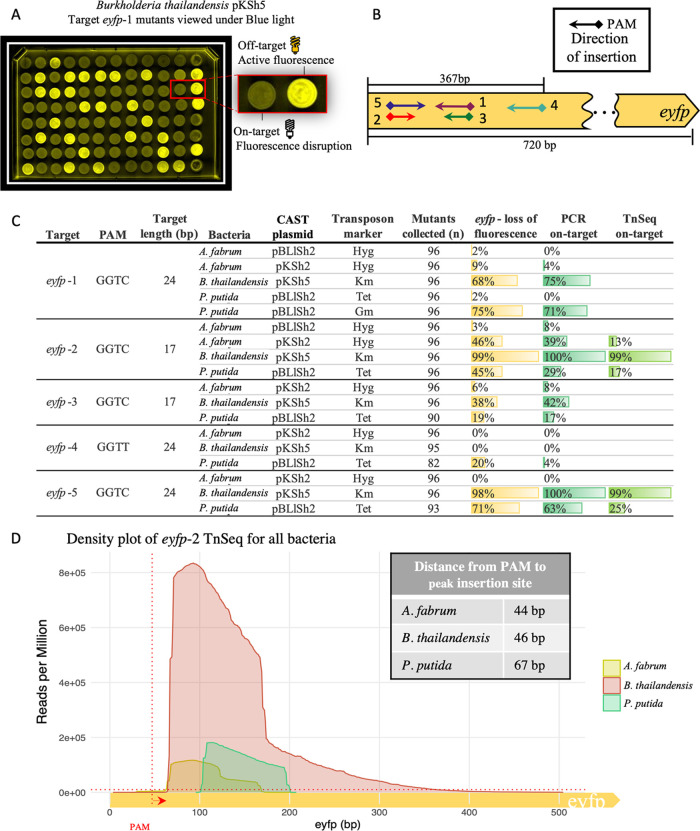
Figure 2.
CAST targeted disruption of eyfp in three Proteobacteria. (A) CAST eyfp targeted integration mutants were selected by the transposon antibiotic resistance marker. The eyfp mutants that lose fluorescence are identified upon exposure to blue light (470 nm). (B) Map of sgRNA targets (arrows), PAM site (diamonds), and insertion direction (arrow point). The sgRNA targeting range is above the gene, and the total gene length is below the gene. (C) Relative frequency of eyfp results in A. fabrum, B. thailandensis, and P. putida. Target name, PAM site, length in bp, the helper plasmid (CAST plasmid), and the transposon resistance marker are given. The loss of fluorescence was calculated with n mutants collected, while genotyping was performed on 24 clones for all targets. The Tn-Seq on-target % was calculated with all reads from each experiment (bin size = 1 Kbp). (D) Density plot of transposon insertions for target eyfp-2 in A. fabrum, B. thailandensis, and P. putida in reads per million (RPM). The x-axis goes from the start of eyfp (0 bp) to 500 bp into the eyfp gene. The vertical dotted red line depicts the start of the PAM site with the arrow pointing to the direction of insertion for target eyfp-2, and the horizontal red dotted line depicts 1 × 104 RPM (bin size = 1 bp).