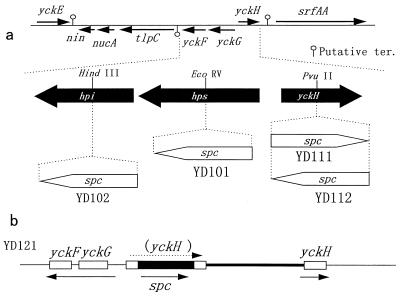
FIG. 1.
Diagram of the chromosomes of wild-type B. subtilis and its mutants. (a) Map of the yckF-yckG (phi-hps) and yckH loci showing the protein coding regions at 32° on the B. subtilis genome (24). Locations and orientations of the coding regions are indicated by thin black arrows, and potential transcription terminators, as proposed in the SubtiList data bank (41), are shown. The hps, phi, and yckH genes are expanded and depicted as thick black arrows below the map. Insertion of a spc cassette (thick white arrow) leading to disruption of hps in strain YD101, phi in YD102, or yckH in YD111 or YD112 is shown. (b) Chromosomal structure of strain YD121, which contains the disrupted and intact yckH genes. Heavy and thin lines depict vector and chromosomal DNA, respectively. Open boxes indicate the yckG, yckF, and yckH genes. The black box shows the spc gene, which disrupts the yckH gene. Thin arrows show the direction of transcription.