Fig. 1.
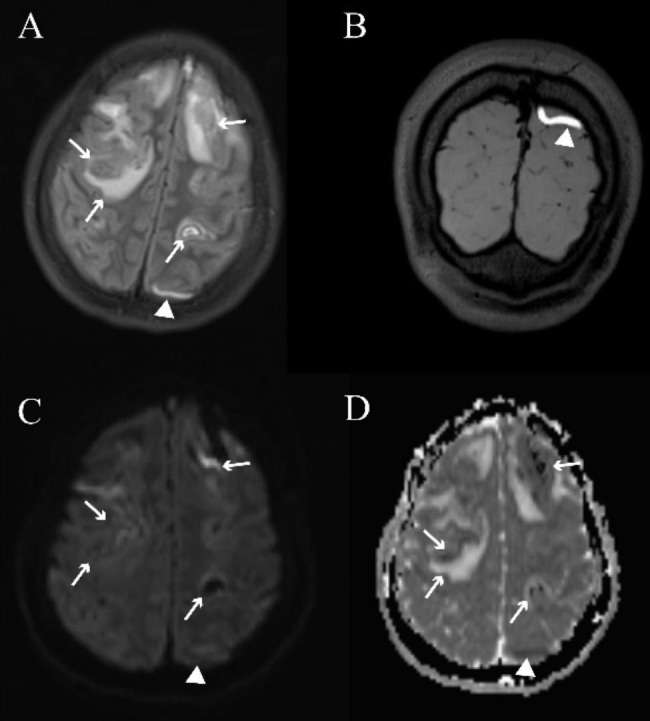
Typical images of cortical vein thrombosis on conventional magnetic resonance imaging and 3D-T1-SPACE scans in a 17-year-old female patient with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. The fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR, A) image shows a cord-like hyperintensity (white arrowheads, representing a subacute thrombosis) of the left cortical vein, which presents as restricted diffusion (white arrowheads) on the diffusion-weighted image (DWI, C) and apparent diffusion coefficient map (ADC, D), consistent with the thrombosed cortical veins on 3D-T1-SPACE (white arrowheads, B). Venous infarction and parenchymal hemorrhage can be observed as mixed signals on FLAIR, DWI, and ADC scans (white arrow)
