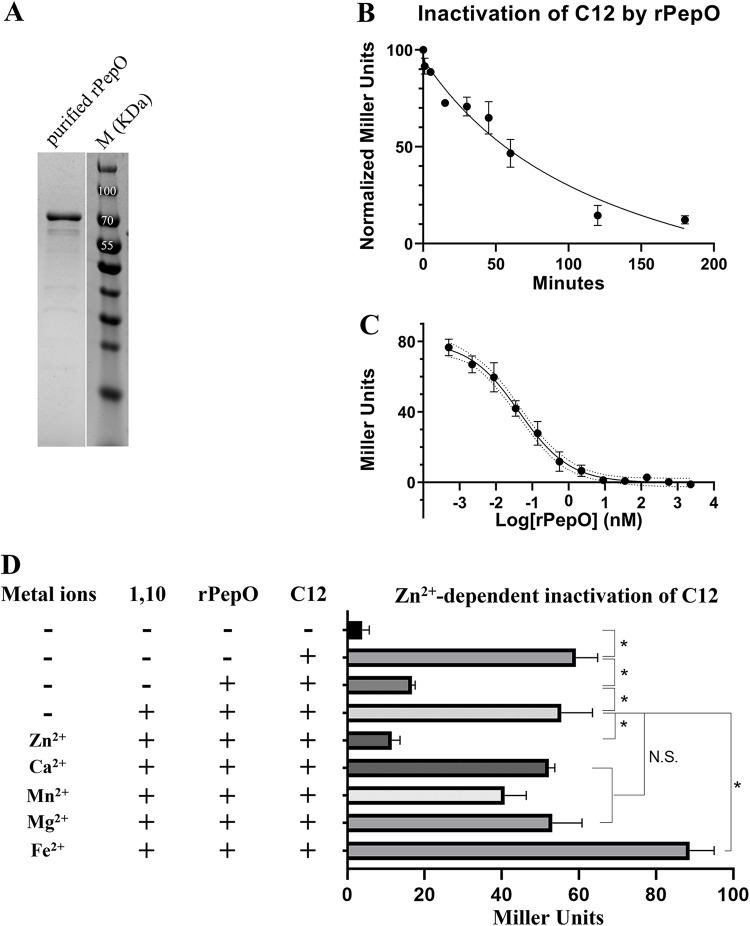
FIG 4.
rPepO degrades C12 in a Zn2+-dependent manner. (A) SDS-PAGE image of purified rPepO (75.74 kDa). (B and C) C12 degradation by rPepO is dependent on reaction time (B) and concentration (C). (D) Comparison of rPepO activity in native, metal-chelated, and metal-supplemented conditions. Data in B to D represent the average of three biological repeats; *, P < 0.05. CDM (glucose) medium was used in the assays.