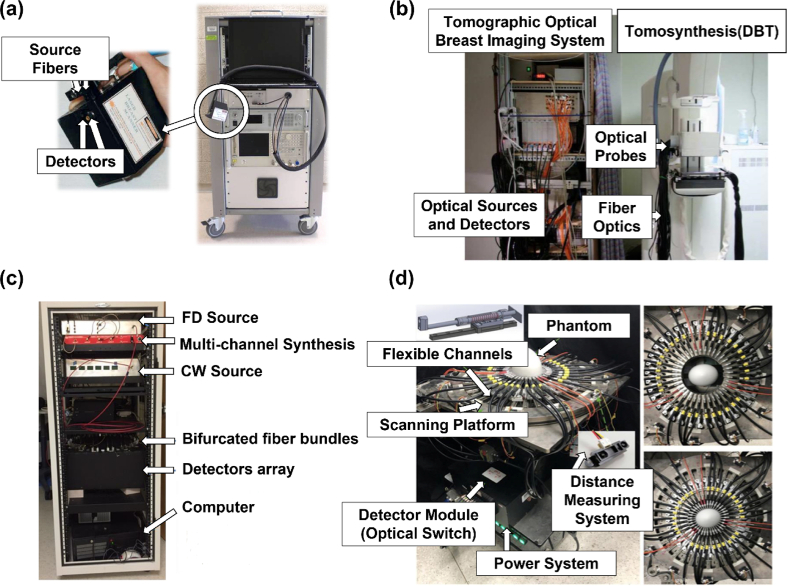
Fig. 1.
Examples of some benchtop-based FD-NIRS systems. (a) The NIRS device described by O’Sullivan et al. The subfigure on the left demonstrates the handpiece placed in contact with the tissue. This figure is taken with permission from [14,19]. (b) The combined Tomographic Optical Breast Imaging (TOBI)/Tomosynthesis (DBT) system described by Fang et al. The TOBI system includes both RF and CW source/detector modules and the fiber optics interface attached to the tomosynthesis system on the right. This figure is taken with permission from [25]. (c) The FD + CW NIRS system for breast cancer diagnosis described by Zhao et al. This figure is taken with permission from [28]. (d) The NIRS system with flexible optical channels for breast tumor detection described by Lee et al. The subfigure on the right demonstrates the maximal (170 mm) and minimal (60 plus 20 mm flexible range) measuring dimensions. This figure is taken with permission from [31].