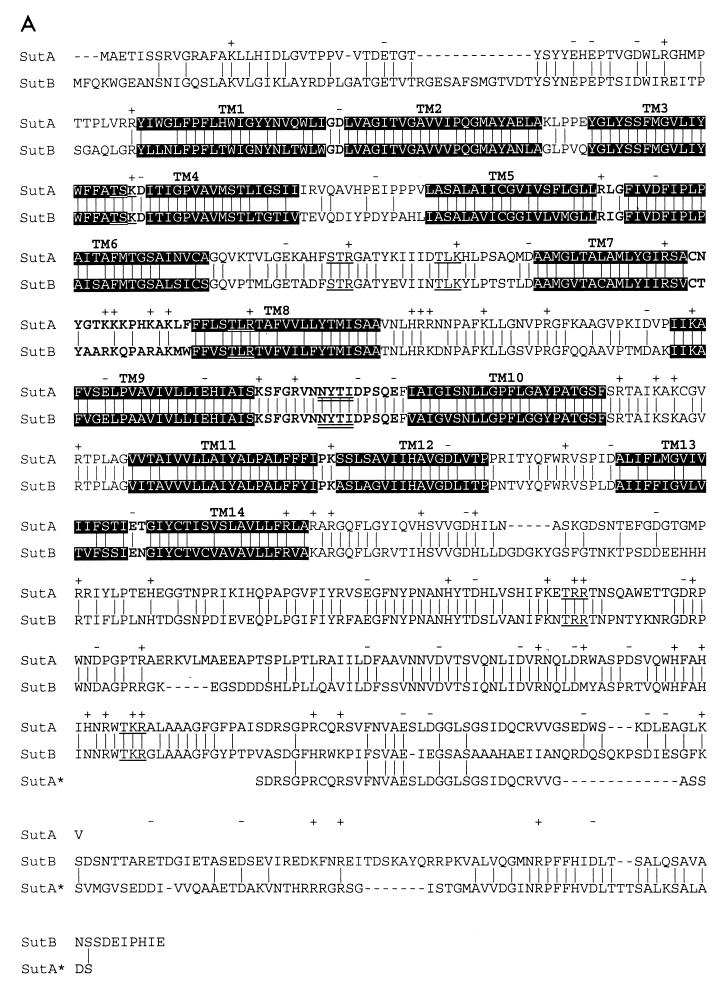
FIG. 5.
(A) Alignment of SutA and SutB amino acid sequences. Indicated are identical residues (|); charges (+, −), predicted protein kinase C phosphorylation sites ([ST]X[RK]) (59), and predicted N glycosylation sites (NX[ST]X, with X1P) (12, 33) which are present in both SutA and SutB; predicted transmembrane helices (black background); and predicted extracellular loops (bold type). Also shown is the alignment of an extended version of SutA, named SutA* (see Fig. 1 and Discussion). Alignments were made with ClustalX (20), and hydropathy profile analysis was done with MemGen version 4.08 (28, 29). (B) Alignment of SutA and SutB amino acid sequences with sequences of some examples of the SulP family of sulfate permeases whose the function has been proven experimentally (except SutA). Shown are the regions around the old sulfate permease motif (44) and the region around the proposed new sulfate permease motif. Alignments were made with the ClustalX program (20). SUTA, P. chrysogenum SutA (accession no. AF163975) (this work); SUTB, P. chrysogenum SutB (AF163974) (this work); CYS14, N. crassa Cys14 (BP23622) (19, 31); SUL1, S. cerevisiae Sul1 (P38359) (9, 49); SUL2, S. cerevisiae Sul2 (S64926 and Z73264) (YLR092w) (9); HVST1, Hordeum vulgare HVST1 (U52867) (51); AST56, Arabidopsis thaliana Ast56 (AB012047 and S74246) (53); DTDST, Homo sapiens DTDST (P50443) (14, 41). The old motif fails to recognize SutB, Sul2, and HVST1.