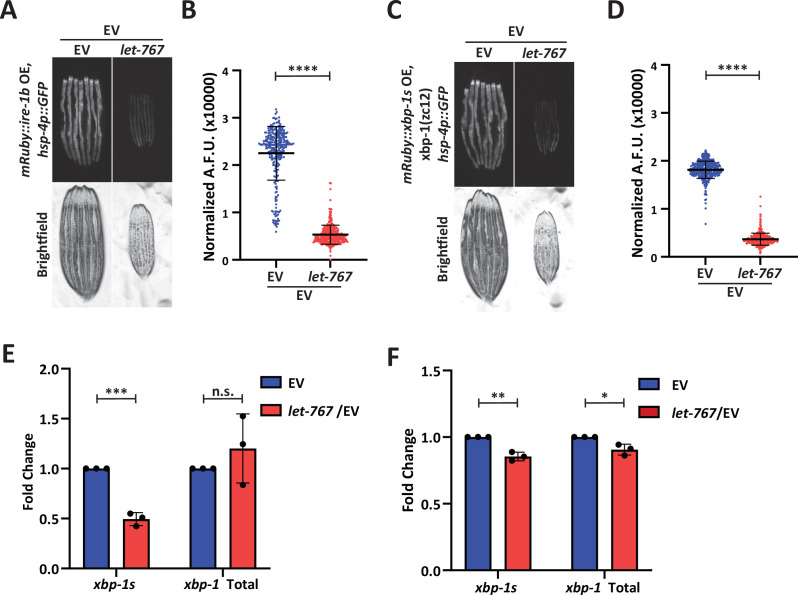
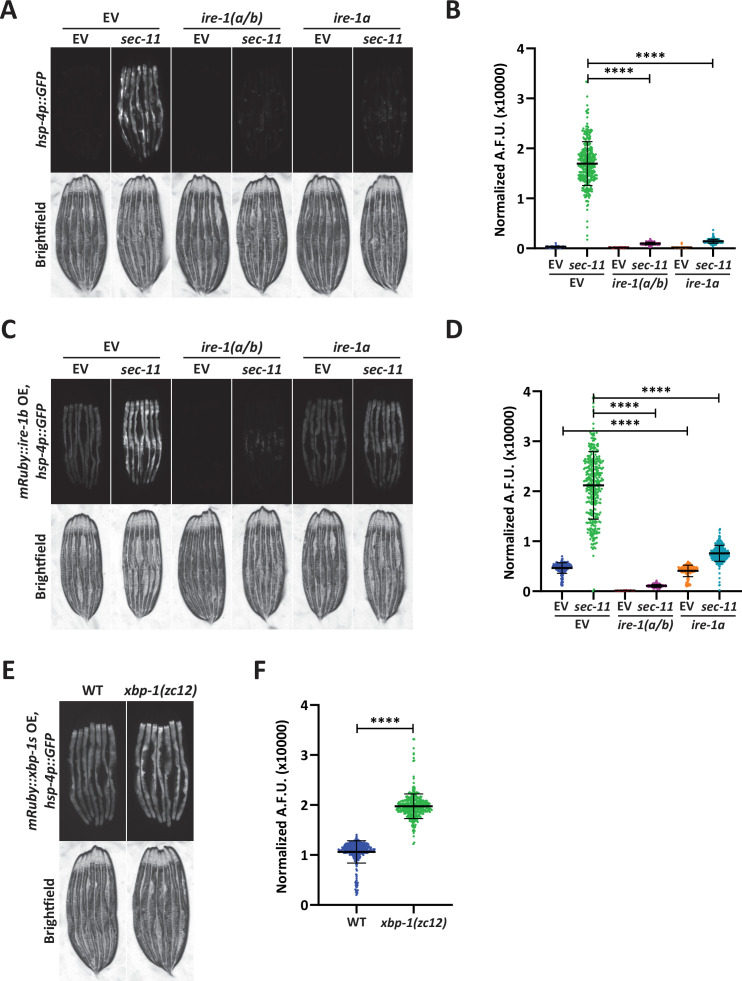
Figure 5. let-767 knockdown impacts UPRER induction independent of xbp-1 splicing.
(A) Fluorescent micrographs of day 1 adult transgenic animals expressing hsp-4p::GFP and intestinal mRuby::ire-1b grown on Empty Vector (EV) or let-767 RNAi mixed with EV in a 1:1 ratio to assay the UPRER induction. (B) Quantification of (A) normalized to size using a BioSorter. Lines represent mean and standard deviation. n=290. Mann-Whitney test P-value ****<0.0001. Representative data shown is 1 of 3 biological replicates. (C) Fluorescent micrographs of day 1 adult xbp-1(zc12) transgenic animals expressing hsp-4p::GFP and intestinal mRuby::xbp-1s grown on EV or let-767 RNAi mixed with EV in a 1:1 ratio to assay the UPRER induction. (D) Quantification of (C) normalized to size using a BioSorter. Lines represent mean and standard deviation. n=398. Mann-Whitney test p-value ****<0.0001. Representative data shown is one of three biological replicates. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR transcript levels of xbp-1s and total xbp-1 from day 1 adult mRuby::ire-1b animals grown from L1 on let-767 RNAi mixed 1:1 with EV. Fold-change compared to EV treated animals.Unpaired t-test p-value ***<0.0005. Error bars indicate ± standard deviation across three biological replicates, each averaged from two technical replicates. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR transcript levels of xbp-1s and total xbp-1 from day 1 adult mRuby::xbp-1s animals grown from L1 on let-767 RNAi mixed 1:1 with EV. Fold-change compared to EV treated animals. Unpaired t-test p-value **<0.005 and *<0.05. Error bars indicate ± standard deviation across three biological replicates, each averaged from two technical replicates. Dots indicate averaged biological replicate values.