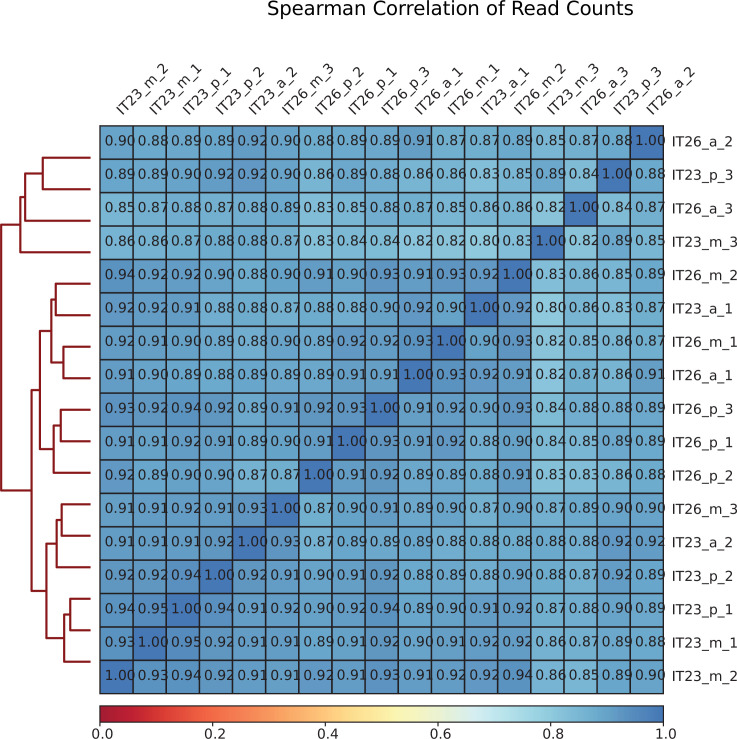
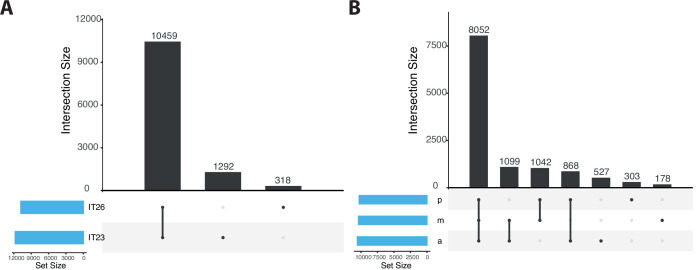
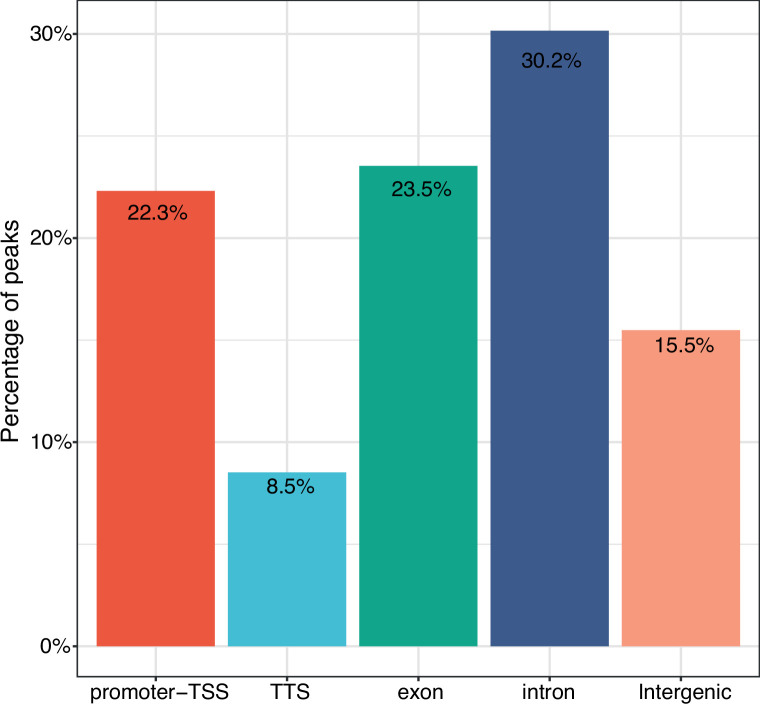
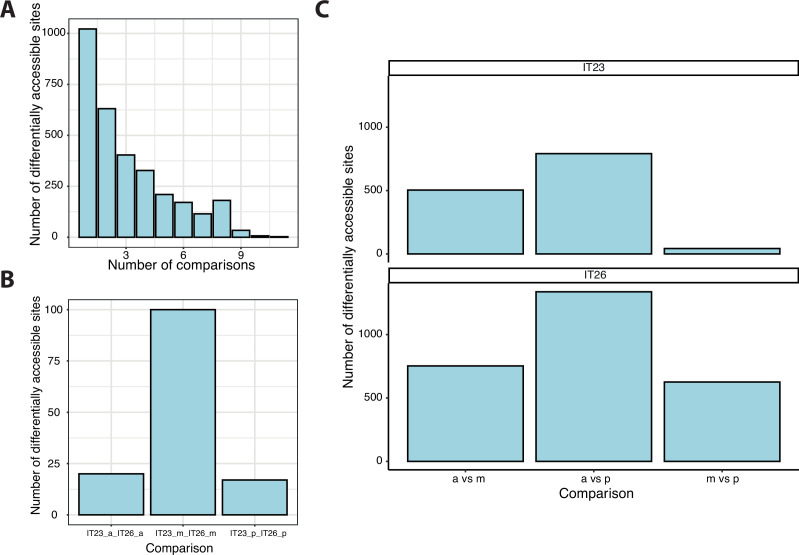
Figure 2. Chromatin accessibility dynamics during anterior-posterior (AP) patterning of the early Tribolium embryo.
(A) Embryos 23–26 hr after egg lay (AEL) (IT23) or 26–29 hr AEL (IT26) were dissected and cut into anterior (a), middle (m), and posterior (p) part. Up: nGFP embryo in the eggshell. Below: dissected and cut nGFP embryo. (A’) A schematic version of (A). (A’’) Representative Tribolium embryo at 23–26 hr AEL (IT23) or 26–29 hr AEL (IT26) in situ stained to visualize the expression of the gap gene hunchback (hb) (green; Hoechst in gray). (B) Principal component analysis (PCA) on the accessibility scores of the most highly accessible and variable sites in the dataset. Only the first two principal components (PC) of the data are represented. The first PC explains 45.3% of the variance in the data, and the second PC, 18.0%. (C, D) Boxplots showing the scores of PC1 and PC2 by space (C) and time (D). The thick line indicates the median (2nd quartile), while the box represents the interquartile range (IQR, 1st to 3rd quartiles). Outliers are shown as dots. (E) Genomic annotation of different classes of chromatin accessible sites: all (consensus) sites, constitutive sites (i.e. consensus sites that are not differentially accessible), all differentially accessible sites, and most specifically accessible sites (i.e. sites differentially accessible in four or more comparisons). (F) K-means clustering of accessibility scores for differentially accessible sites. Accessibility scores have been z-score scaled for each site.