Figure 4. Multiple types of immunological synapses (IS) variants were observed and well-predicted by the base model.
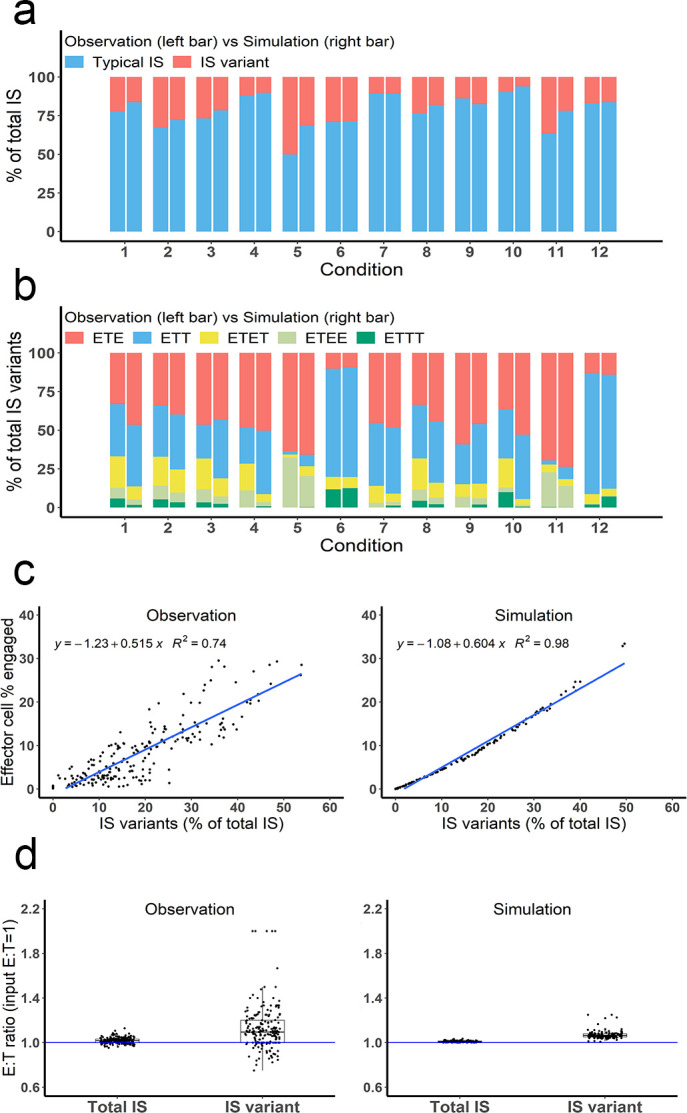
In total, six types of IS were quantified, including typical IS (ET), ETE, ETT, ETET, ETEE, and ETTT. (a) The fraction of typical IS and variants under different conditions; (b) The composition of IS variants (ETE, ETT, ETET, ETEE, ETTT) under different conditions; (c) The positive correlation between the fraction of IS variants (% of total IS) and total IS formation (effector cell % engaged). The formula and R2 of linear regressions are shown. (d) The E:T ratios involved in total IS and IS variants. Experimental setup: Condition 1, 2 X, E:T(1), CD3(L), CD19(M), 100 ng/mL, 60 min; Condition 2, 4 X, E:T(1), CD3(L), CD19(M), 100 ng/mL, 60 min; Condition 3, 2 X, E:T(1), CD3(H), CD19(M), 100 ng/mL, 60 min; Condition 4, 2 X, E:T(1), CD3(L), CD19(L), 100 ng/mL, 60 min; Condition 5, 4 X, E:T(6), CD3(L), CD19(M), 100 ng/mL, 60 min; Condition 6, 4 X, E:T(0.17), CD3(L), CD19(M), 100 ng/mL, 60 min; Conditions 7–12 are the same as Conditions 1–6, except with lower bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) concentrations (20 ng/mL).
