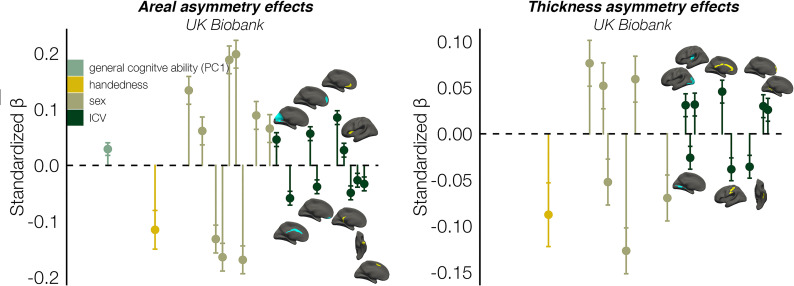
Figure 7. Asymmetry associations with general cognitive ability (first principal component [PC1]), handedness, sex, and intracranial volume (ICV) in UKB, in clusters exhibiting population-level areal (upper) and thickness asymmetry (lower).
(A, D) Significance of associations (negative logarithm; corrected [p<7.4e–5] and uncorrected threshold [p=0.01] shown by dotted and non-dotted line, respectively). X-axis displays the test for each cluster-association. As maximum sample size was used to test each association, effects of general cognitive ability were tested in separate models with fewer observations (N=35,198; separated association plots) than handedness, sex and ICV (N=37,569). (C) Visualization of the found association between leftward areal asymmetry in the large supramarginal cluster with general cognitive ability. The line of null association is shown for comparison (dotted) (B, E) Right plots denote effect sizes, 95% confidence intervals (error bars) and cortical location of associations surpassing Bonferroni-corrected significance. Individual AIs in rightward clusters were inversed. Right handers and females are coded 0, such that a negative effect for general cognitive ability / handedness / sex / ICV / reflects less asymmetry in higher cognition / left handers / males / larger brains. Associations with ICV are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Yellow and blue clusters denote leftward and rightward asymmetries, respectively.