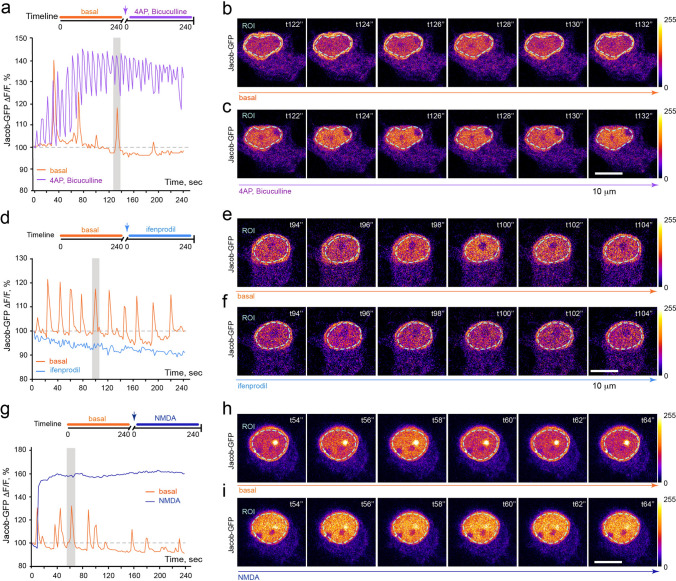
Fig. 5.
Synaptic activity controls the subnuclear redistribution of Jacob in a GluN2B-dependent manner. a–c As revealed by time-lapse imaging, enhanced synaptic activity changes the pattern of Jacob’s residing time. a Schematic represents the timeline of the experiment. The graph represents changes in fluorescent intensities within indicated ROI over time. Depicted are confocal image frames corresponding to 10 s of recording before (b) and after the treatment (c) with 4AP/bicuculline (grey bar in a). Scale bar = 10 μm. d–f Application of ifenprodil abolished the subnuclear redistribution of Jacob during basal glutamatergic transmission. g–i Treatment of neurons expressing Jacob-GFP with bath NMDA resulted in plateau-like accumulation of Jacob in the nucleoplasm