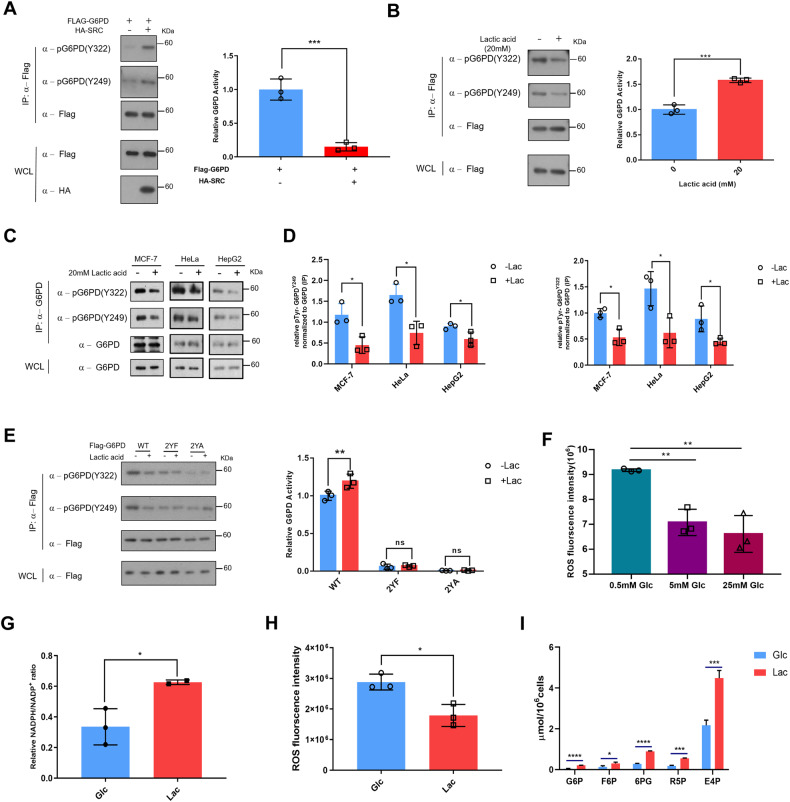
Fig. 4. Lactic acid modulates the catalytic properties of G6PD and switches cells to a reprogrammed PPP mode through GSTP1.
A G6PD activity upon SRC over-expression as measured by catalytic activity of immuno-purified/Flag peptide-eluted Flag-tagged G6PD (Left panel). Results are mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. The p value was analyzed by Student’s t test. ***p = 0.0009. Right panel showed that the phosphorylation of G6PD under SRC over-expression. B MCF-7 cells were transfected with Flag-G6PD for 24 h and switched to glucose-deprived media with or without 20 mM lactic acid for another 12 h. Flag-G6PD was immunopurified, the phosphorylation status (Right panel) and the activity (Left panel) were determined. Relative enzymatic activity was presented as mean ± SD of triplicate independent experiments and analyzed by unpaired Students’ test. *p = 0.0138. C, D MCF-7 cells/HeLa cells/HepG2 cells were treated with or without 20 mM lactic acid. The lysates were immunoprecipitated with G6PD antibody (C). The phosphorylation level was determined through normalization with total G6PD (D). Two other independent experiments are shown in supplementary materials. *p < 0.05. E Lactic acid reduces Y249 and Y322 phosphorylation of WT but not its mutants in MCF-7 cells (Left panel), and the activities of 2YF and 2YA versus the WT were determined (Right panel). Two-way ANOVA was applied to analyse the results. **p (WT -lac VS WT +lac) = 0.0038. F The ROS levels were determined under different concentrations of glucose. **p < 0.01. G Lactic acid increases the NADPH/NADP+ ratio. The NADPH/NADP+ ratios were determined at OD 570 nm. Data are presented as mean ± SD of triplicate experiments and analyzed by unpaired Students’ test. *p = 0.0459. H Lactic acid reduces the ROS level. Data are presented as mean ± SD of triplicate experiments and analyzed by unpaired Students’ test. *p = 0.0131. I Abundances of key PPP metabolites were determined, n = 3. Results are mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. The p-value was analyzed by Student’s t-test.