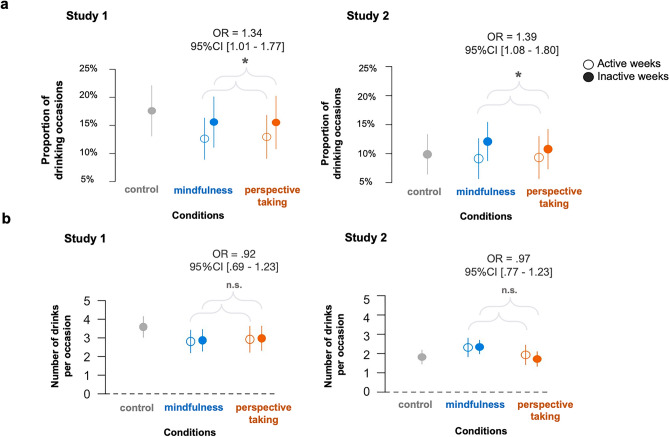
Figure 2.
Psychological distance reminders reduce drinking frequency but do not influence amount. a. Collapsing across experimental conditions, participants in the mindfulness and perspective-taking groups were less likely to drink following active intervention reminders relative to following control reminders in Study 1 (left) and Study 2 (right). b. We found no differences in the number of drinks consumed on alcohol use occasions following active intervention reminders, relative to following control reminders across both studies, Study 1 (left) and Study 2 (right). Note: figure presents raw data for illustration. Dots present the mean and the error bars present 95% confidence intervals.