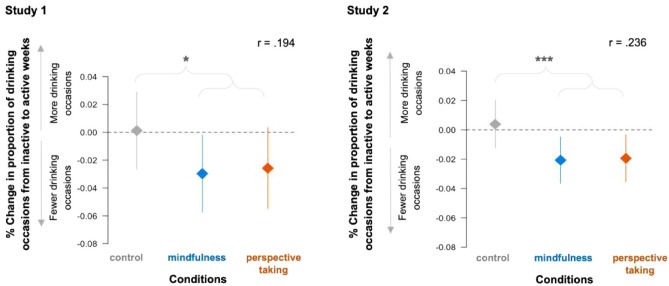
Figure 3.
Intervention reminders change drinking frequency among participants in the intervention conditions vs. control. Participants in the distancing conditions—mindfulness and perspective-taking—reported greater behavior change, i.e., drank less frequently on active vs. inactive weeks, relative to the change among participants in the control condition who received non-intervention reminders, in Study 1 (left) and Study 2 (right). Negative change scores suggest intervention consistent behavior change, or decreases in the frequency of drinking occasions.