Figure 2.
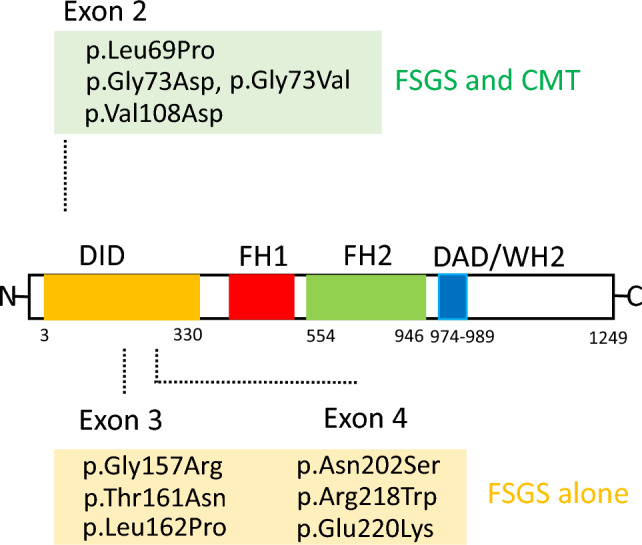
Locations of variants in the INF2 domain structure. The distribution of variants in INF2 functional domains is shown. Variants in exon 2 were found in individuals with a dual phenotype of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) and FSGS, whereas those in exon 3 and exon 4 were identified in patients with FSGS alone. INF2 is a large multi-domain protein composed of three functional domains: Diaphanous inhibitory domain (DID, orange), formin homology (FH) domains FH1 and FH2 (red and green), and diaphanous autoregulatory domain (DAD, blue). The DID interacts with the DAD within the same molecule (intramolecular autoinhibition) as well as with other actin regulators (e.g., small GTPase and mDia). The FH domains mediate both actin polymerization and depolymerization. Domain positions are according to UniprotKB-Q27J81. WH2: WASP homology 2; mDia: mammalian Diaphanous-related formin 1.
