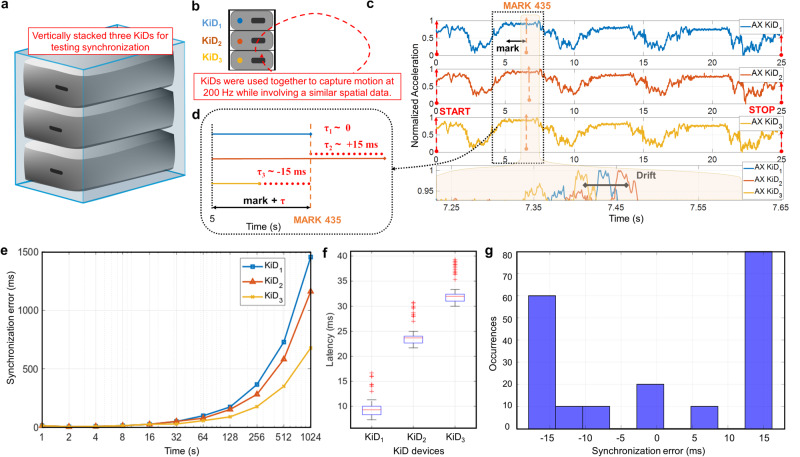
Fig. 3. Multiple device evaluation without synchronization algorithm.
a KiDs are vertically stacked upon each other, i.e., KiDi where i is 1…3 for evaluating the multiple device performance. b While data capturing, all these KiDs share the same spatial attributes, allowing it more straightforward to analyze the temporal attribute. c Acceleration profiles from three KiDs show the 200 Hz motion data with a similar spatial attribute. d The temporal shifts (τi where i is 1…3 indicate temporal shifts in each wearable device) within KiDs provide incorrect time information; thus, they provide inaccurate time stamping. e Frequency drift among three devices KiDi where i is 1…3 when connected to the remote system without synchronization for 1024 s. f Example of KiDs latency, when connected with three devices, due to the Bluetooth transmission for a synchronized message that affects synchronization, the mean values found to be KiD1 = 9.5 ± 1.762 ms, KiD2 = 23.8 ± 2.01 ms, KiD3 = 32.5 ± 2.37 ms. g The average synchronization error in these wearables is 30 ms, i.e., the frequency drift within devices and the Bluetooth latency contribute to this indeterministic error causing inaccurate time interpolation while experimenting.