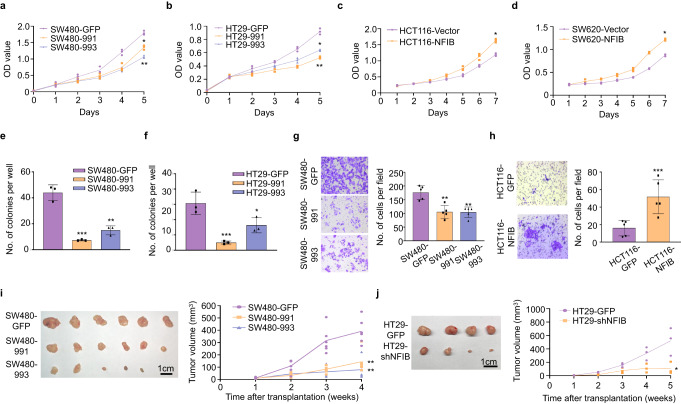
Fig. 1. NFIB promotes CRC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro, and growth in vivo.
a–d CCK-8 assays show that knockdown of NFIB inhibited the proliferation of SW480 and HT29 cells, whereas overexpression of NFIB enhanced the proliferation capacity of SW620 and HCT116 cells. e, f Colony formation experiments showed that NFIB knockdown inhibited the proliferation of SW480 and HT29 cells. g, h Transwell assays indicated that knockdown of NFIB inhibited the migratory and invasive ability of SW480 cells, while overexpression of NFIB promoted the migratory and invasive capacity of HCT116. i, j The size of xenograft tumors in the NFIB-knockdown group was significantly smaller than in the control group. The growth curve of xenograft tumors in the NFIB-knockdown group was slower than in the control group. Bar graph data are presented as the mean ± SD; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.