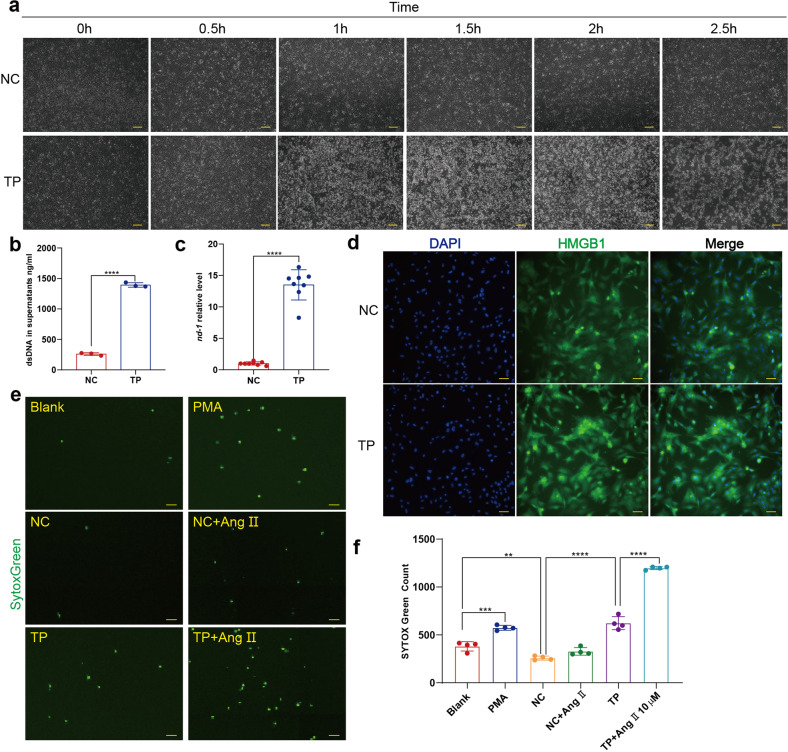
Fig. 5.
Supernatants of tachy-paced cardiomyocytes could induce NETosis. a Neonatal rat cardiomyocyte could not survive from long period of tachy-pacing. Cardiomyocytes in 6-well plate paced by C-Pace EP Culture Stimulator of 1 Hz (NC) or 6 Hz (TP) were observed and imaged by microscopy every 30 minutes. Scale bar: 200 μm. b Analysis of dsDNA with PicoGreen in the supernatants of tachy-paced cardiomyocytes and normal control (n = 3). cfDNA in supernatants of tachy-paced cardiomyocytes and normal control were measured with PicoGreen incubated in 96-well plate by fluorescence microplate reader. c Analysis of mtDNA in the supernatants of tachy-paced cardiomyocytes and normal control (n = 8). d HMGB1 was translocated from nucleus to cytoplasm in tachy-paced cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes in 6-well plate were stained for DNA (blue) and HMGB1 (green). Scale bar: 20 μm. e, f Rat neutrophils undergoing NETosis measured by Celigo analysis in the presence or absence of PMA, Ang II and supernatants of cardiomyocytes paced with frequency of 1 Hz or 6 Hz (n = 4). Rat neutrophils in 96-well plate were stained for all DNA (blue) and cfDNA (green). Hoechst single positive cell was defined as the living, while Hoechst and SYTOX Green double positive cell with decondensed nucleus was defined as cell undergoing NETosis. Scale bar: 500 μm. TP, tachy-pacing, HMGB1 high mobility group box 1. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Data were presented as mean ± SD