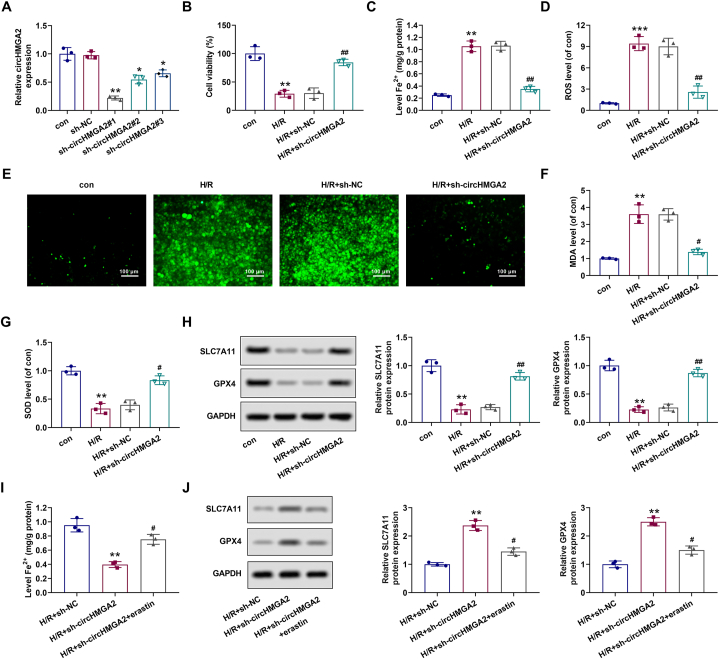
Fig. 2.
Depletion of circHMGA2 suppressed ferroptosis in H/R-induced HCMs. (A) The efficiency of shRNA-mediated circHMGA2 knockdown (sh-circHMGA2#1, #2, #3) in H/R-induce HCMs was detected by RT-qPCR. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. sh-NC. (B) Effect of circHMGA2 knockdown on the proliferative ability in H/R-induced HCMs was detected by CCK-8 assay. **p < 0.01 vs. con; ##p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-NC. (C) Effect of circHMGA2 knockdown on the ferrous ion (Fe2+) content in H/R-induced HCMs was detected by iron assay kit. **p < 0.01 vs. con; ##p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-NC. (D–E) Effect of circHMGA2 knockdown on ROS levels in H/R-induced HCMs was detected by DCFH-DA staining. Quantifications were as described in (D) and the staining was shown in (E). ***p < 0.001 vs. con; ##p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-NC. (F–G) Effect of circHMGA2 knockdown on the levels of MDA (F) and SOD (G) in H/R-induced HCMs was detected by ELISA assays. **p < 0.01 vs. con; #p < 0.05 vs. H/R + sh-NC. (H) Effect of circHMGA2 knockdown on the levels of ferroptosis-related proteins (GPX4 and SLC7A11) in H/R-induced HCMs was detected by western blotting. **p < 0.01 vs. con; ##p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-NC. (I) Effect of erastin (ferroptosis inducer) on the ferrous ion (Fe2+) content in H/R-induced HCMs transfected with sh-circHMGA2 was detected by iron assay kit. **p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-NC; #p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-circHMGA2. (J) Effect of erastin on the levels of ferroptosis-related proteins (GPX4 and SLC7A11) was detected by western blotting in H/R-induced HCMs transfected with sh-circHMGA2. **p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-NC; #p < 0.01 vs. H/R + sh-circHMGA2.