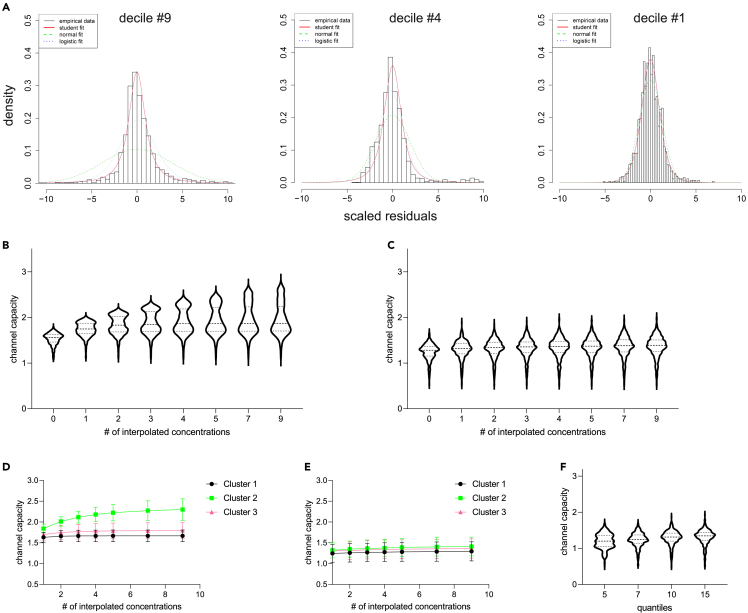
Figure 4.
New algorithm for channel capacity estimation based on response probability calculation from peaks with similar heights provides more robust results
(A) Distributions of the residuals obtained for similar response magnitudes as on the Figure 1C, but using pooling by deciles of average peak heights, are considerably more homogeneous, and provide more robust fits.
(B and C) Violin plots showing the shapes and medians of channel capacity distributions obtained at different degrees of interpolation for the concentration-based approach (B) and the peak-based one (C).
(D and E) One of the cell clusters identified in Figure S2 drives the gradual increase of the channel capacity estimate on more interpolation steps in the concentration-based approach (D) but not in the peak-based approach (E).
(F) Channel capacity distributions calculated on the splitting of residuals into different numbers of quantiles show that these parameters have limited influence on the outcome when the peak-based approach is used.