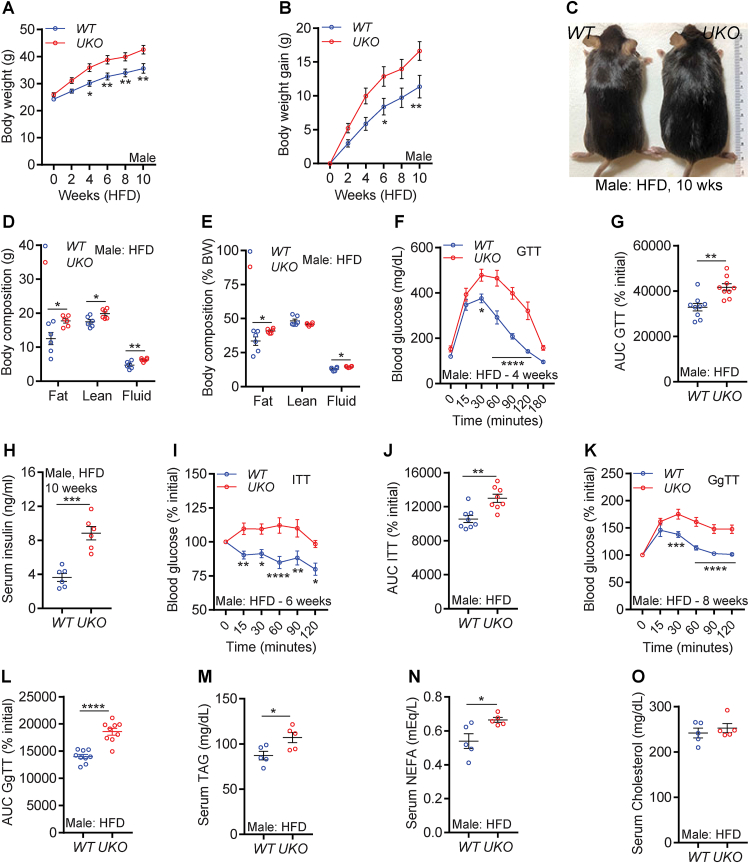
Figure 2.
Ube4A deletion augments HFD-induced obesity and insulin resistance in male mice.
A-B. Weekly body weight and weight gain of HFD-fed male mice (n = 13/cohort).
C. Representative image of HFD-fed male mice after conclusion of the study.
D-E. Total and percent (over total body weight) body composition of HFD-fed male mice (N = 6/cohort).
F. Raw values of the GTT in HFD-fed male mice (n = 9/cohort). GTT was performed in 4-week-HFD-fed mice.
E. AUC values of the rate (percent of 0 time point) of decrease in blood glucose levels in a GTT in HFD-fed male mice (n = 9/cohort).
G. Serum insulin levels in 5 h-fasted male mice after 10-week of HFD feeding (n = 6/cohort).
H. Rate (percent of 0 time point) of decrease in blood glucose levels in an insulin tolerance test (ITT) in HFD-fed male mice (n = 8/cohort). ITT was performed in 6-week-HFD-fed mice.
I. AUC values of the ITT presented in Figure 2H (n = 9/cohort).
sJ. Rate (percent of 0 time point) of increase in blood glucose levels in a glucagon tolerance test (GgTT) in HFD-fed male mice (n = 9/cohort). GgTT was performed in 8-week-HFD-fed mice.
K. AUC values of the GgTT presented in Figure 2J (n = 9/cohort).
L-N. Serum levels of TAG, NEFA and total cholesterol in HFD-fed male mice.
The number of mice (n) used are presented as individual datapoints. Mean ± s.e.m. shown within dot plots. For multiple comparisons, two-way ANOVA with Holm-Šidák multiple comparison test and for two independent data sets, Two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.