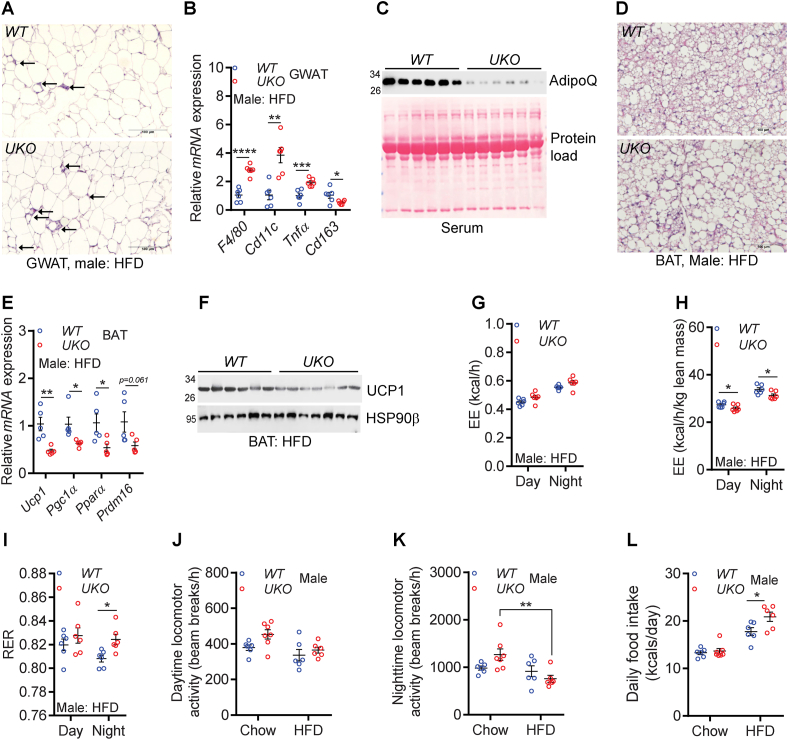
Figure 4.
HFD-fed male UKO mice exhibit increased adipose tissue metabolic dysfunction.
A. Representative histological images (20X, scale bar: 100 μm) of GWAT of HFD-fed mice. Arrows indicate crown-like structures.
B. Relative mRNA levels of M1 and M2 macrophage markers in the GWAT of HFD-fed male mice (N = 6/cohort).
C. Serum AdipoQ levels in HFD-fed male mice (N = 6/cohort). Serum samples were denatured and run on a denatured SDS-PAGE to detect monomeric AdipoQ.
D. Representative histological images (20X, scale bar: 100 μm) of HFD-fed mouse BAT.
E. Relative mRNA expression of the thermogenic machinery in the BAT of HFD-fed male mice (N = 5–6/cohort).
F. Levels of UCP1 protein in the BAT of HFD-fed male mice (N = 6–7/cohort).
G. EE (whole mouse) in HFD-fed mice (N = 6/cohort).
H. EE (normalized by lean mass) in HFD-fed mice (N = 6/cohort).
I. RER in HFD-fed mice (N = 6/cohort).
J-K. Average daytime and nighttime activity in chow- and HFD-fed mice (N = 6–7/cohort).
L. Average daily caloric intake in chow- and HFD-fed mice (N = 6–7/cohort).
The number of mice (n) used are presented as individual datapoints. Mean ± s.e.m. shown within dot plots. For multiple comparisons, two-way ANOVA with Holm-Šidák multiple comparison test and for two independent data sets, Two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.