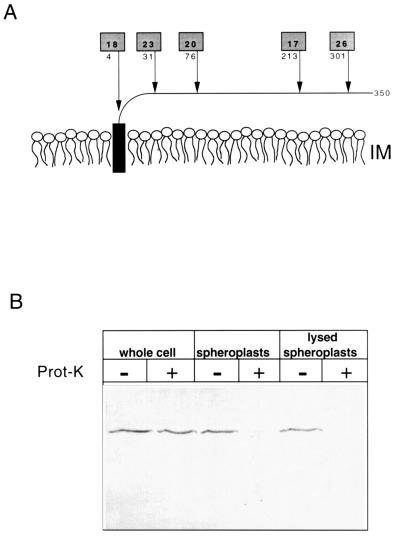
FIG. 2.
ApbE is periplasmically located. (A) The predicted monotopic structure of ApbE anchored in the outer leaflet of the inner membrane lipid bilayer is schematically shown. Arrows indicate the location of active alkaline phosphatase (PhoA) fusions to ApbE encoded by pApbE1, and the number below the shaded box indicates the amino acid of ApbE that immediately proceeds the fusion junction. The numbers in the shaded boxes represent the relative PhoA activity (in units per minute per optical density at 650 nm) of each fusion compared to a control containing an out-of-frame PhoA fusion. (B) Immunoblot showing the proteinase K accessibility of chromosomally encoded ApbE in whole cells, spheroplasts, and lysed spheroplasts. Samples were treated with (+) or without (−) proteinase K (100 μg/ml). The proteins in each sample (equivalent to 0.05 A650) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with a 1:5,000 dilution of ApbE antisera.