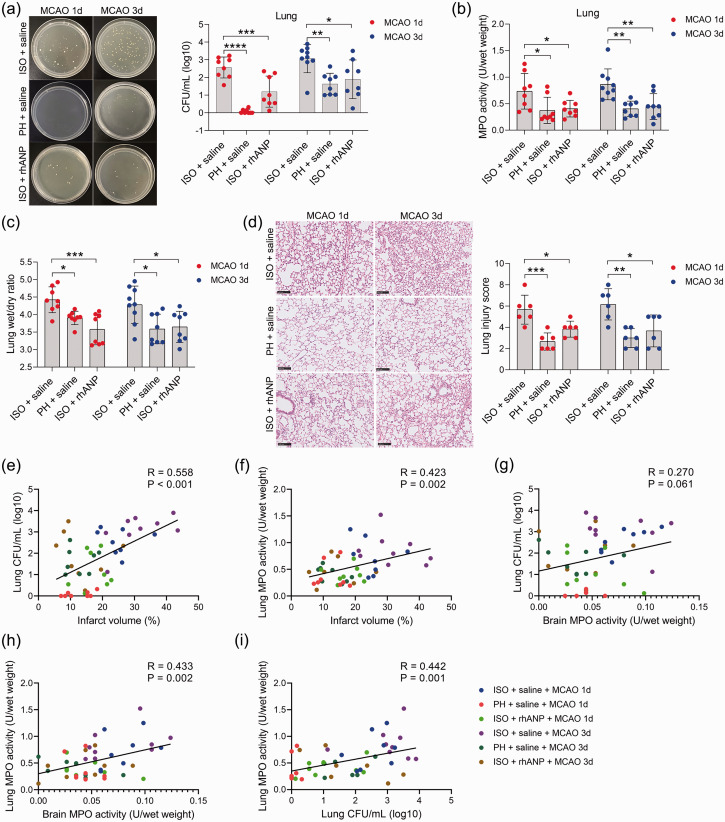
Figure 2.
Pre-stroke ISO aggravated stroke-associated pneumonia, which could be reversed by rhANP. (a) Bacterial loads in the lungs of post-stroke mice. (b) Pulmonary MPO activity. (c) Pulmonary edema assessed by measuring the wet lung weight normalized per body weight and wet/dry lung ratio. (d) Representative H&E sections of lung and histological injury scores. Scale bar =100 µm. (e) Positive correlation (r = 0.558, P < 0.001) between brain infarct volume and the number of pulmonary CFUs. (f) Positive correlation (r = 0.423, P = 0.002) between brain infarct volume and pulmonary MPO activity. (g) Positive correlation (r = 0.27, P = 0.061) between brain infarct volume and the number of pulmonary CFUs. (h) Positive correlation (r = 0.433, P = 0.002) between cerebral MPO activity and pulmonary MPO activity and (i) Positive correlation (r = 0.558, P < 0.001) between the number of pulmonary CFUs and pulmonary MPO activity. Data are presented as individual values plus means ± SDs (n = 6–9/group). Comparisons were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Newman–Keuls multiple comparison tests. Correlations were analyzed by Pearson correlation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. CFU, colony-forming units; ISO, isolated housing; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PH, pair housing; rhANP, recombinant human atrial natriuretic peptide.