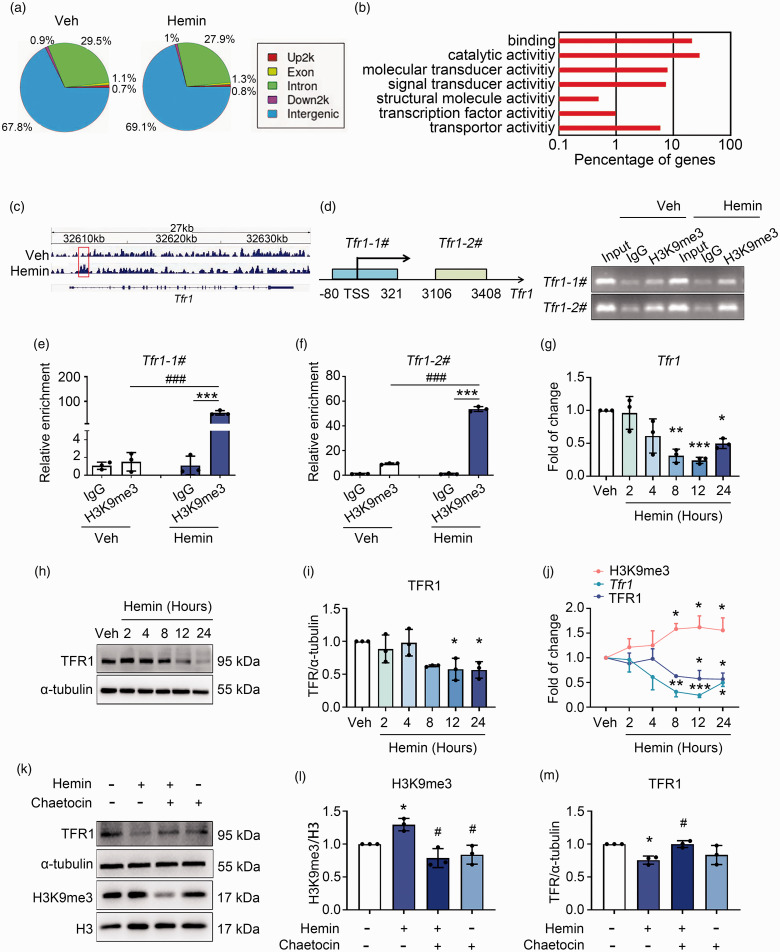
Figure 3.
H3K9me3 represses Tfr1 expression during neuronal ferroptosis. (a) Genomic distribution of the H3K9me3 in vehicle and hemin treated N2A cells that detected with ChIP-Seq. (b) GO analyses of annotated targets of H3K9me3 histone modification in hemin treated group based on ChIP-Seq data. (c) Integrated genome viewer of H3K9me3 ChIP-seq tracings for the Tfr1 locus in vehicle and Hemin groups. Increased enrichment of H3K9me3 signal on the Tfr1 gene is shown in red rectangle. (d) Left: the schematic diagram shows the primers designed to perform ChIP assays at the Tfr1 locus. TSS, transcription start site. Right: DNA Continued.electrophoresis using agarose gels followed by ChIP assays. (e, f) ChIP assays were analyzed with Real-time qPCR. Results are expressed as fold enrichment to IgG. (g) N2A cells were treated as indicated, and the mRNA level of Tfr1 was assessed with Real-time RT-PCR. GAPDH serves as an internal control. (h, i, k–m) N2A cells were treated as indicated, and proteins were extracted for Western blot. α-tubulin serves as an internal control. Representative images (h, k) and quantifications (i, l, m) are shown. (j) The levels of H3K9me3, Tfr1 mRNA, and TFR1 protein in N2A cells at different time points upon hemin or vehicle treatment were compared. Results are shown as scatter plots or line charts (Mean ± SD). n = 3 independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons tests (e, f) or One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons tests (g, i, j, l, m) was used. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs vehicle or corresponding IgG. #p < 0.05, vs Hemin.