Figure 4.
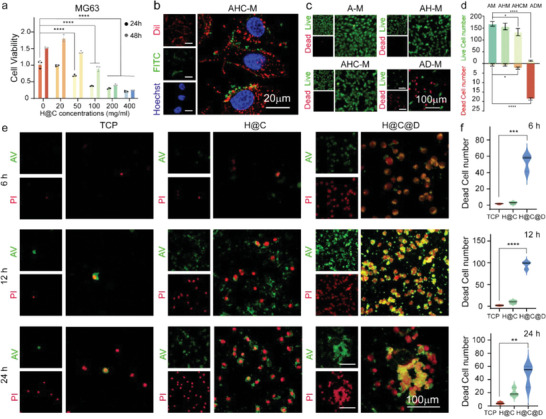
The synergistic antitumor ability of the antibody‐modified nHAP and Dox as indicated by MG63 cell apoptosis. a) CCK‐8 assay of MG63 cells cultured with different concentrations of H@C for 24 and 48 h. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. The p values were calculated using two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's comparison test (n = 3; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001). b) Colocalization of H@C and MG63 cell membrane after 24 h. H@C detached from the living material. Red, green, and blue indicate the Dil‐stained cell membrane, FITC‐labeled H@C, and Hoechst‐stained nuclei. c) Live/dead staining of MG63 cells after co‐culture with the living materials for 12 h in a Transwell system. The concentration of nanorods contained in the living materials was 100 µg mL−1. d) Live and dead cell numbers were determined by live/dead staining of MG63 cells after co‐culture with the living materials for 12 h in a Transwell system and analysis by ImageJ. The p values were calculated using one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's comparison test (n = 3; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001). e) AV/PI staining of MG63 cells after culture with 100 µg mL−1 H@C and H@C@D for 6, 12, and 24 h. Apoptotic cells were stained green with AV‐Fluor 488, and dead cells were stained red with PI. f) Dead cell numbers as determined by AV/PI staining of MG63 cells and analyzed by ImageJ. The p values were calculated using one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's comparison test (n = 3; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001).
