Fig. 5.
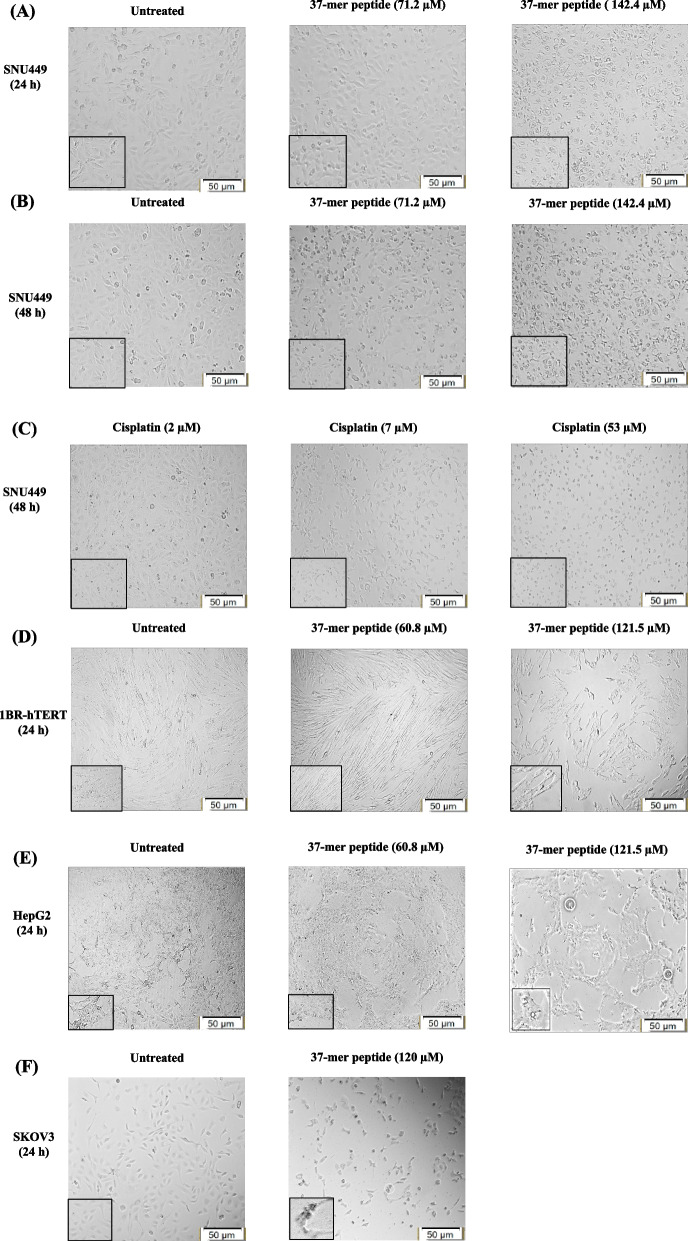
Peptide effect on cellular morphology of SNU449, 1Br-hTERT, HepG2, and SKOV3 cell lines. A The lowest (71.2 μM) and one of the highest (142.4 μM) concentrations of peptide treatment on SNU449 cell line at 24 h. Untreated SNU449 cells are compact small spindle-shaped adherent epithelial cells. Treatment with 71.2 μM 37-mer peptide showed cells forming circular shapes and detachment of adherence surface. At higher peptide concentration, cells appeared to be surrounded by debris and form condensed cell detachments. B The lowest (71.2 μM) and one of the highest (142.4 μM) concentrations of the peptide on SNU449 cell line at 48 h treatment. Untreated cells in 48 h culture appeared similar to 24 h culture. Treatment with 71.2 μM of the peptide exhibited cells forming rounded sparse distribution. A higher concentration of treatment (142.4 μM) led to the aggregation of ruptured cells forming circular floating detachments. C Three concentration points in Cisplatin treatment gradient of SNU449 cells for 48 h: 2 μM, 7 μM, and 53 μM concentration. Induction of 2 μM cisplatin had minimal effect on SNU449 cell morphology compared to untreated cells. 7 μM Cisplatin treatment appeared to halt cell proliferation without changing cellular morphology. High concentration (53 μM) of cisplatin showed excessive cell rounding and reduced cell count. D The lowest (60.8 μM) and the highest (121.5 μM) concentrations of peptide treatment on 1BR-hTERT cell line at 24 h. Untreated cells formed elongated, aligned spindle-shaped morphology. The treatment of 1BR-hTERT cells with 60.6 μM appeared to break up cells without causing visible cell death. High concentration (121.5 μM) exposure displayed fragmented cells while losing the spindle elongated morphology, with some cells forming circular shrink appearance. E The 2nd highest (60.8 μM) and the highest (121.5 μM) concentrations of 37-mer peptide treatment on HepG2 cell line at 24 h. Untreated HepG2 cells formed a monolayer of an irregular epithelial-like shape. Treatment of HepG2 cells with 60.8 μM caused cells to become sparse, with fragmented growth, while not showing signs of cell rounding. With the highest concentration of treatment, the HepG2 monolayer appeared to be sparse and significantly more fragmented than untreated cells. Additionally, highlighted section included rounded and floating cells, surviving cells do not resemble original cell morphology. F SKOV3 cell images of untreated and peptide-treated cells (120 μM). SKOV3 cells formed smaller circular spindle square formations. Administration of 120 μM of peptide caused cells to change morphology and become sparse, circular, and condensed, characteristic of dead cells. The highlighted section shows rounded detached morphed cells with surrounding debris. Cell images are processed at magnification scale of 50 μm