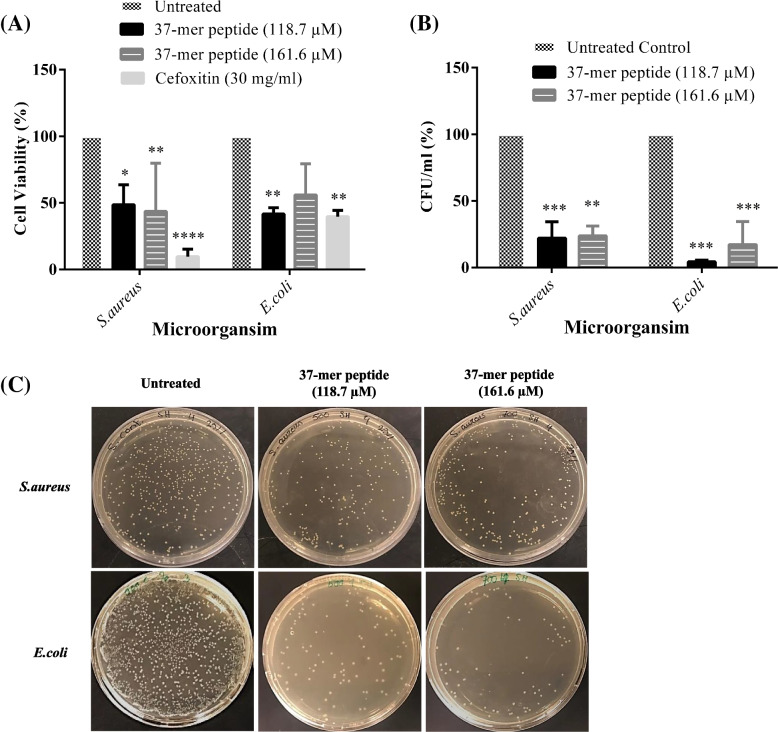
Fig. 9.
Antimicrobial activity of S. aureus and E. coli was evident with 37-mer peptide treatment. Statistical representation of peptide antimicrobial activity on S.aureus and E.coli. A Effect of 161.6 μM and 118.7 μM of peptide treatment on viable S. aureus and E. coli bacteria using microdilution assay. Cell viability was determined via absorbance measurements at 600 nm. Cefoxitin (30 mg/ml) was considered a positive control. Peptide treatment resulted in significant loss of viability, approximately 50% or lower, in both gram positive (S. aureus) and gram-negative (E. coli) bacterial strains. B Colony formation unit of S. aureus and E. coli cells was significantly debilitated (approximately 25%) by both concentrations. S. aureus specifically, showed an approximate 20% (118.7 μM) and 25% (161.6 μM) decrease in CFUs overnight exposure, respectively. E. coli CFU count displayed an approximate 5% and 15% respective decrease with medium and high treatment, respectively (*** P < 0.001, ** P < 0.01, n = 3). C Representative images of agar plates showing viable colonies of S. aureus and E. coli after overnight culture (106 dilution factor)