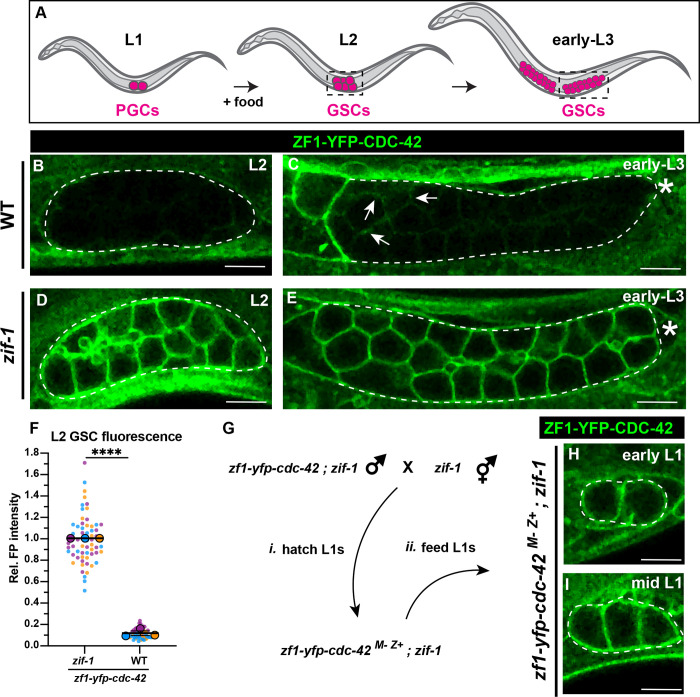
Figure 3. ZIF-1 mediates degradation in proliferative germ cells during early larval development.
(A) Schematic of early larval germline development: Upon feeding, PGCs (magenta) re-enter the cell cycle and become undifferentiated germline stem cells GSCs (also magenta). GSCs continue to proliferate as development progresses. L2 and early L3 stages shown, dashed boxes represent the region of the worm imaged. (B) ZF1-YFP-CDC-42 is absent from wild-type L2 larval GSCs (dashed lines). (C) Expression of ZF1-YFP-CDC-42 in wild-type is first detected in early L3 GSCs, but is restricted to the proximal gonad (arrows), ZF1-YFP-CDC-42 signal remains weak near the distal gonad (asterisks). (D-E) ZF1-YFP-CDC-42 is expressed throughout the gonad in zif-1 mutant L2 and early L3 GSCs. (F) Quantification of L2 GSC ZF1-YFP-CDC-42 fluorescence in WT and zif-1 mutants, normalized to expression in zif-1 mutants. (G) Crossing scheme to introduce ZF1-YFP-CDC-42 zygotically in PGCs. (H-I) ZF1-YFP-CDC-42 expression in fed L1 larval PGCs. Individual data points from three independent color-coded biological replicates are shown as small dots, the mean from each experiment shown as a larger circle, the mean of means as a horizonal line, and the S.E.M as error bars. ****p ≤ 0.0001, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bar, 5μm.