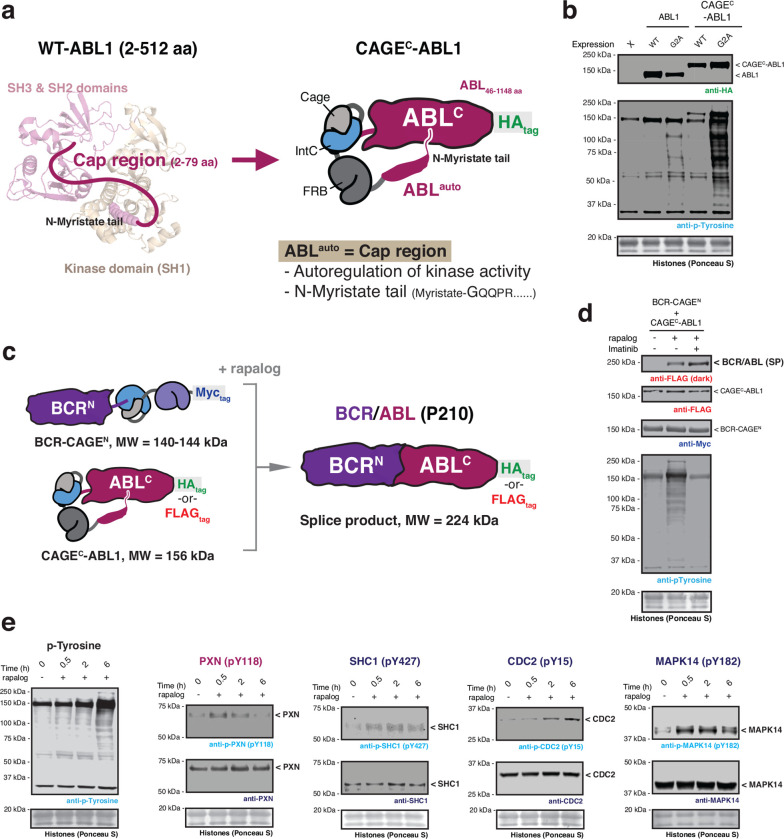
Fig. 3 |. Post-translational generation of BCR/ABL allows dissection of dynamic cellular phosphorylation events.
a, Left – crystal structure of ABL1 kinase (PDB: 2FO0). The unstructured cap region which connects the SH3 domain to the N-terminal myristoyl group is shown as a cartoon. The myristoyl modification binds to an allosteric site in the C-lobe of the kinase domain. Right – schematic depicting the design of the autoinhibited CAGEC-ABL1 construct. b, Immunoblots of the basal tyrosine phosphorylation levels in HEK293T cells expressing wild-type or G2A mutant of ABL1 and CAGEC-ABL1 constructs. c, Schematic of proximity-triggered CPS between complementary BCR-CAGEN and CAGEC-ABL1 constructs to generate the BCR/ABL oncofusion. Molecular weights of the splice product and CAGE constructs are indicated. The CAGEC-ABL1 construct is kept in an inactive state prior to splicing through use of a N-myristoyl control element. d, Immunoblots of BCR/ABL (FLAG-tag) splice product (SP) and global tyrosine phosphorylation levels in HEK293T cells co-expressing BCR-CAGEN (Myc-tag) and CAGEC-ABL1 (FLAG-tag). Cells were treated with DMSO or rapalog (100 nM) or rapalog and Imatinib (10 μM) for 18 hours prior to analysis. e, Immunoblots of the tyrosine phosphorylation levels in HEK293T cells co-expressing BCR-CAGEN and CAGEC-ABL1. Cells were treated with rapalog (100 nM) for indicated time-points before analysis with the indicated antibodies. Data in (b), (d), and (e) are representative of n=3 independent experiments. CAGEN refers to ‘NpuNCage-FKBP,’ and CAGEC refers to ‘ABLauto-FRB-NpuCCage’.