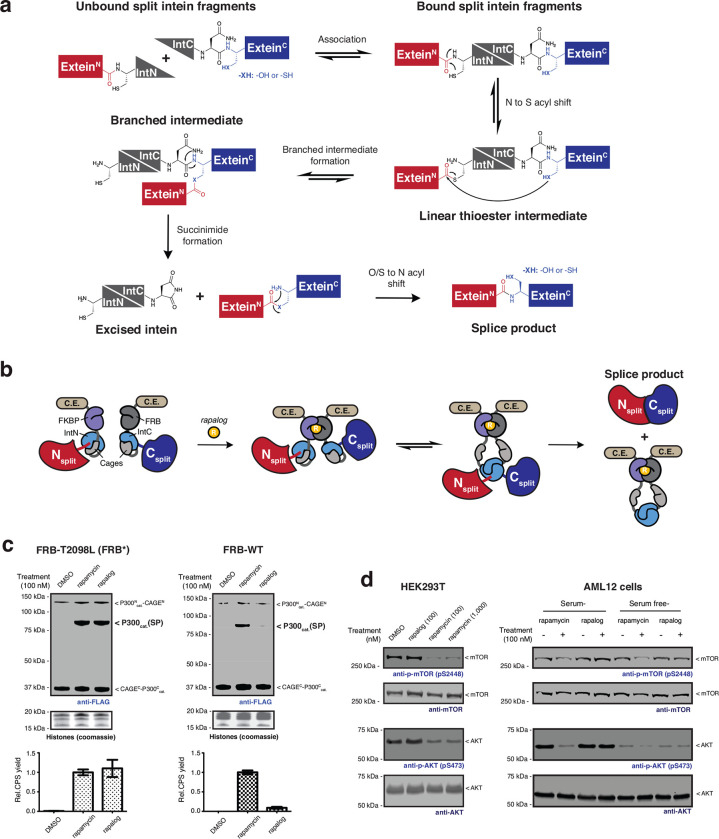
Extended Data Fig. 1 |. CAGE modules generate the splice products in live cells by non-toxic rapamycin analog treatment.
a, Mechanism of the protein trans-splicing reaction by split inteins. b, Schematic of the CPS reaction using CAGE modules. Rapalog-induced FKBP-FRB dimerization is followed by a domain swapping event that yields an active split intein complex. c, Left – Immunoblots (top) of splice product (FLAG-tag) generation via CAGE modules incorporating FRB T2098L mutant (FRB*) in HEK293T cells. Cells were treated with DMSO, rapamycin (100 nM), or non-toxic rapamycin analog AP21967 (rapalog, 100 nM) for 18 hours. The bar graph below shows quantified splice product levels following the indicated treatments normalized to the product band intensity of rapamycin (bottom) (n=4, mean and s.e.m.). Right – as in the left-hand panel but employing wild-type FRB in the CAGE constructs. d, Immunoblots of phosphorylation levels at mTOR S2448 and AKT S473 sites in HEK293T cells (left) and AML12 cells (right) treated with DMSO, rapalog, or rapamycin at the indicated dose for 18 hours. Data in (d) is representative of n=3 independent experiments. CAGEN refers to ‘NpuNCage-FKBP,’ and CAGEC refers to ‘FRB-NpuCCage’ in (c).