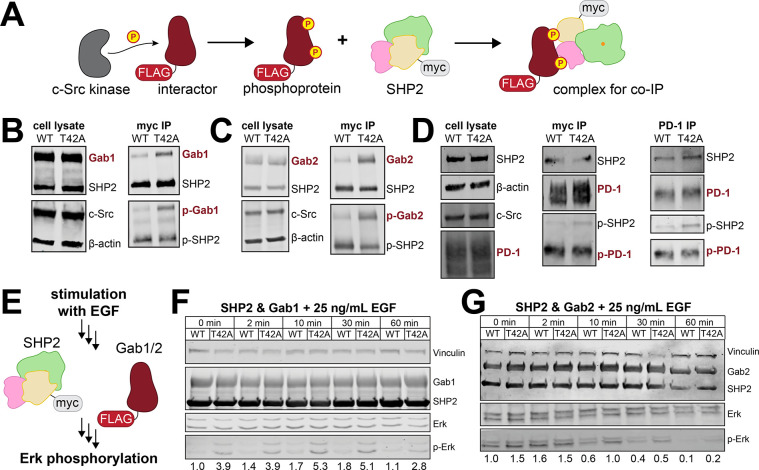
Figure 7. Enhanced cellular interactions and signal transduction by the SHP2 T42A mutation.
(A) Schematic diagram depicting the co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) experiments with SHP2 and either Gab1, Gab2, or PD-1 in HEK293 cells. The interactor proteins are phosphorylated by a hyperactive form of c-Src kinase. SHP2 co-immunoprecipitation experiments with (B) Gab1, (C) Gab2, and (D) PD-1, demonstrating that SHP2T42A binds tighter to these phosphoproteins than SHP2WT. In each case, SHP2 was immunoprecipitated via its myc-tag. Co-immunoprecipitation of the interacting protein was detected using an α-FLAG antibody for Gab1/Gab2 and a PD-1-specific antibody for PD-1. For PD-1, the experiment was also conducted by immunoprecipitating PD-1 and detecting co-immunoprecipitation of SHP2 using an α-myc antibody. (E) Schematic depiction of EGF stimulation and phospho-Erk signaling experiments in the presence of co-expressed SHP2 and either Gab1 or Gab2. (F) Comparison of phospho-Erk levels in response to EGF stimulation in cells expressing Gab1 and either SHP2WT or SHP2T42A. (G) Comparison of phospho-Erk levels in response to EGF stimulation in cells expressing Gab2 and either SHP2WT or SHP2T42A. For panels (F) and (G), the numbers below the blots indicate phospho-Erk levels relative to the 0 minute sample with SHP2WT.