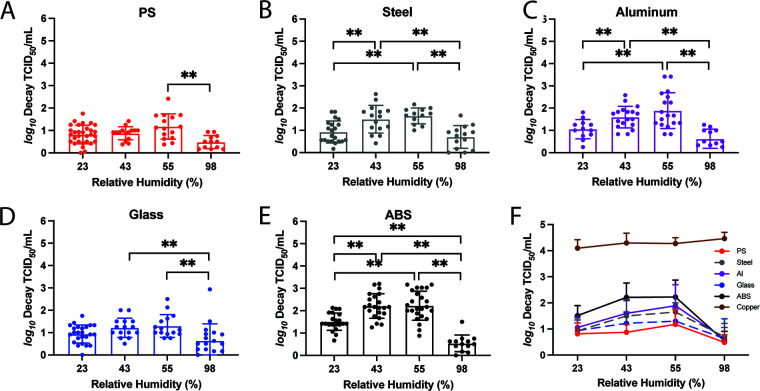
FIG 2.
The impact of RH on H1N1pdm09 stability is surface dependent. The stability of H1N1pdm09 in 10 1-μL droplets on each material was tested at a range of RHs: 23%, 43%, 55%, and 98%. The infectivity decay of the virus after 2 h on (A) PS plastic, (B) stainless steel, (C) aluminum, (D) glass, and (E) ABS plastic was calculated as described for Fig. 1. Virus propagated from at least three different HBE cultures was tested under each condition. Each data point represents a single replicate, and the results are means and standard deviations. Two-way ANOVA, using surface material and RH as the variables, with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test was performed on the results in panels A to E to analyze the effect of RH on the virus decay. **, P < 0.01 (see also Table 1). (F) The means and standard deviations of virus decay on each of the surfaces in panels A to E and on copper were plotted against the RH.