Figure 1: Components of the Hippo pathway in Drosophila/Mammals, C. elegans and Yeast (S. cerevisiae):
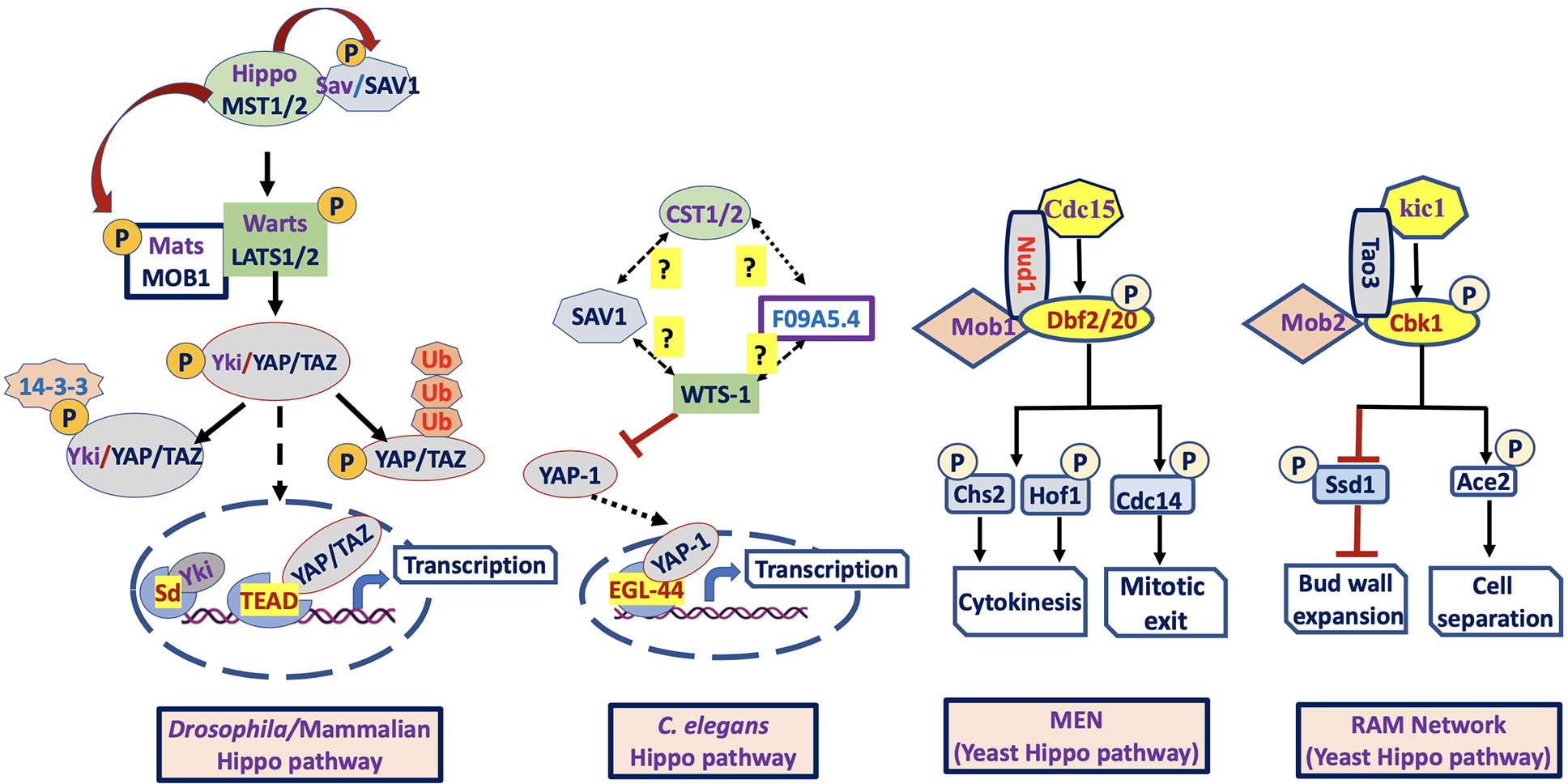
In Drosophila/Mammals (left figure), together with Sav/SAV1 and Mats/MOB1, the Hippo/MST1/2 (kinase) phosphorylates and activates Warts/LATS1/2 (kinase) that in turn phosphorylates and inactivates Yki/YAP/TAZ (downstream effector). Inactivation of hippo pathway results in Yki/YAP/TAZ nuclear translocation and interaction with Sd/TEAD or other transcription factors to induce target gene expression. In C. elegans (middle figure), the role of upstream regulator CST1/2 (Hippo homolog) on the activation of F09A5.4 (Putative Mats homolog), SAV1 (Salvador homolog) and WTS-1 (Warts homolog) is unknown. However, the WTS-1_YAP-1_EGL-44 axis is conserved, supported by the same role as Warts_Yorkie_Scalloped or LATS_YAP_TEAD axis of Hippo pathway. In Yeast (S. cerevisiae), mitotic exit network (MEN) is similar to canonical LATS pathway (Salvador/warts/Hippo system), whereas RAM network is similar to non-canonical NDR pathway (furry/tricomered/Hippo system). The core components of MEN include, Cdc15 (MST/Hippo -related kinase domain), and the protein kinases Dbf2 and Dbf20 (Paralogous protein LATS-family kinases) and Mob1 (co-activator). The core components of RAM network include Kic1 (MST/Hippo related protein kinase), Cbk1 (Ndr/LATS family-related protein kinase), Tao3 (scaffold protein), Mob2, and Hym1 (activator), Ace2 and Ssd1 (downstream effectors).
