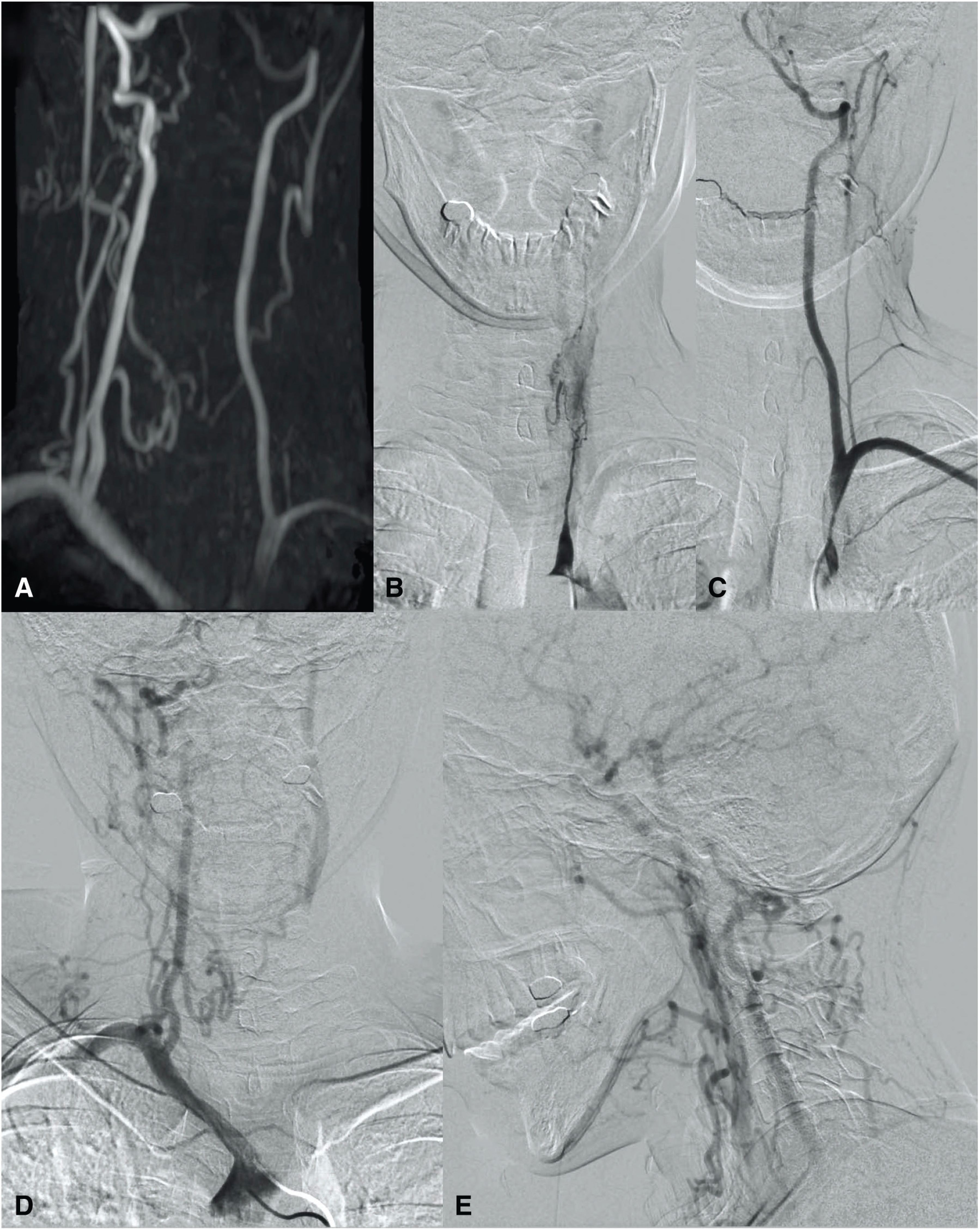
Fig. 1. (A) Cervical MRA. Bilateral CCA were occluded, but collateral blood flow into bilateral ECA developed and the bilateral ICA was visualized. (B) Left common carotid artery angiography. The left common carotid artery was tapered and occluded. (C) Left subclavian artery angiography. The left subclavian artery exhibited severe stenosis at the origin. (D) Innominate artery angiography (AP view). (E) Innominate artery angiography (lateral view). The right ascending carotid artery was flowing into the right ECA, and the right ICA was flowing antegradely via the right common carotid artery bifurcation. The right inferior thyroid artery was flowing into the left superior thyroid artery, then into the left ECA. The left common carotid artery was occluded in the middle, and its distal end was blinded and stagnant. The left ICA was flowing antegradely. CCA: common carotid arteries; ECA: external carotid artery; ICA: internal carotid artery; MRA: magnetic resonance angiography.