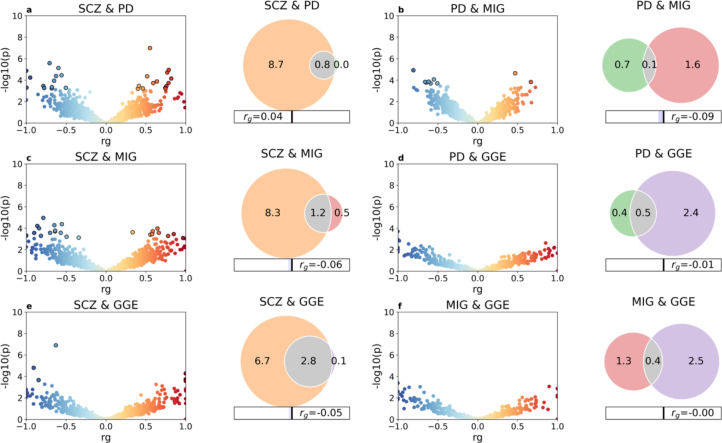
Fig. 4 |. Genetic overlap beyond global genetic correlations.
LAVA local correlations and MiXeR-modeled genome-wide genetic overlap for selected disorders schizophrenia (SCZ), Parkinson’s disease (PD), migraine (MIG) and genetic generalized epilepsy (GGE). To the left, volcano plots of local genetic correlation coefficients (rho) against −log10 p-values for each pairwise analysis per locus estimated using LAVA34 (See Supplementary Table 7 for full results). Dots encircled in black represent significantly correlated loci after false discovery rate correction. To the right, Venn diagrams showing the number (in thousands) of shared and disorder-specific variants and the global genetic correlation (rg) estimated using MiXeR33 (See Supplementary Fig. 3 and Supplementary Table 6 for full results). The total polygenicity for each disorder represents the estimated number of variants required to explain 90% the SNP-based heritability.