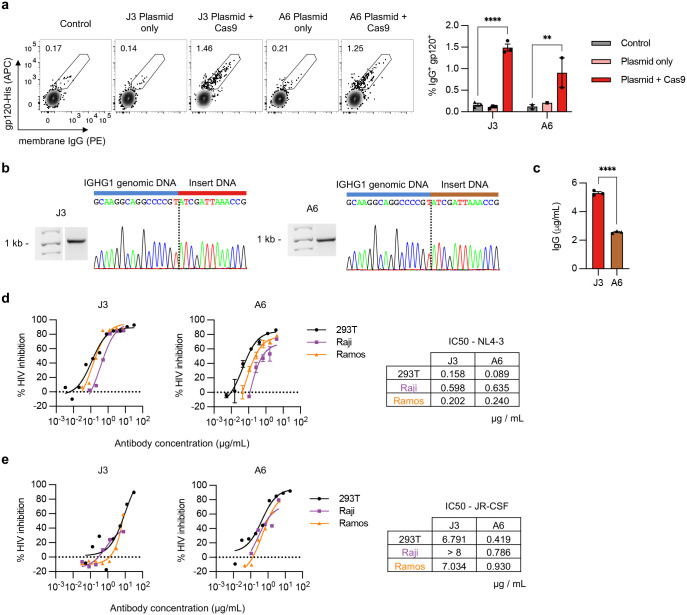
Figure 2. Engineering B cell lines to express anti-HIV HCAbs.
(a) Raji B cells were edited with sg05 Cas9 RNPs plus plasmid homology donors encoding J3 (n = 3) or A6 (n = 1–2) VHH cassettes. Surface expression of resulting HCAb BCRs was measured 1 week later by flow cytometry, staining for surface IgG expression and gp120 binding. Representative plots are shown, together with summary data. (b) J3 or A6 edited Raji cells were FACS-sorted based on surface IgG (see Extended Data Fig. 2c), and the enriched population was subjected to in-out PCR and Sanger sequencing of PCR bands to confirm precise insertions. The dotted line indicates the predicted sg05 cut site. Uncropped gel is available in Supplementary Fig. 3b. (c) Sorted J3- or A6-edited Raji cells were seeded at 106 cells/mL and IgG secretion measured 2 days later by ELISA (n = 3). (d) J3 or A6 HCAbs (n = 3 technical replicates) from supernatants of sorted populations of edited Raji and Ramos cells were analyzed for anti-HIV neutralization activity against X4-tropic HIV strain NL4–3 using the TZM-bl assay. Control recombinant HCAb supernatants were obtained from transfected 293T cells. Neutralization curves are shown for serial dilutions of each HCAb and IC50s were calculated from the curves. (e) Anti-HIV neutralization activity determined as in (d), against R5-tropic HIV strain JR-CSF. Error bars show mean ± SEM. Statistics in panel (a) were performed by 2-way ANOVA. ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.