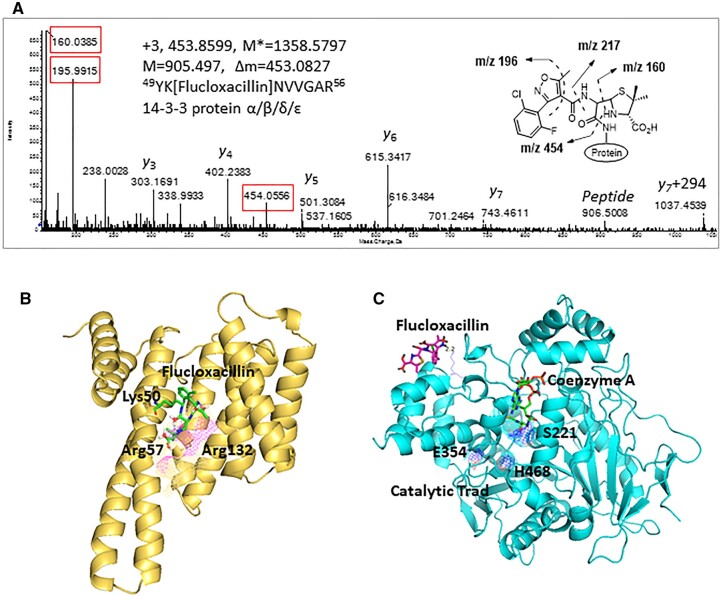
Figure 4.
Covalent binding of flucloxacillin to hepatic proteins. A, A representative MS/MS spectrum shows an adduct was formed on 14-3-3 protein (YK[Flucloxacillin]NVVGAR)—M* = observed flucloxacillin-modified peptide mass, M = theoretical unmodified peptide mass. Characteristic fragment ions from flucloxacillin are highlighted (red boxes). B, Molecular modeling predicts that covalent binding of flucloxacillin to Lys50 on 14-3-3 proteins (PDB code 4E2E) would clash with Arg57 and Arg132 (purple mesh), the key amino acids involved in phosphorylation of binding partner proteins. C, Flucloxacillin (purple) covalently binds to multiple lysine residues on liver carboxylesterase 1, which are distant from the catalytic domain (blue mesh, PDB code 2H7C) and the ligand (coenzyme A, green) binding pocket. Images are illustrated by PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.3 Schrödinger, LLC.).