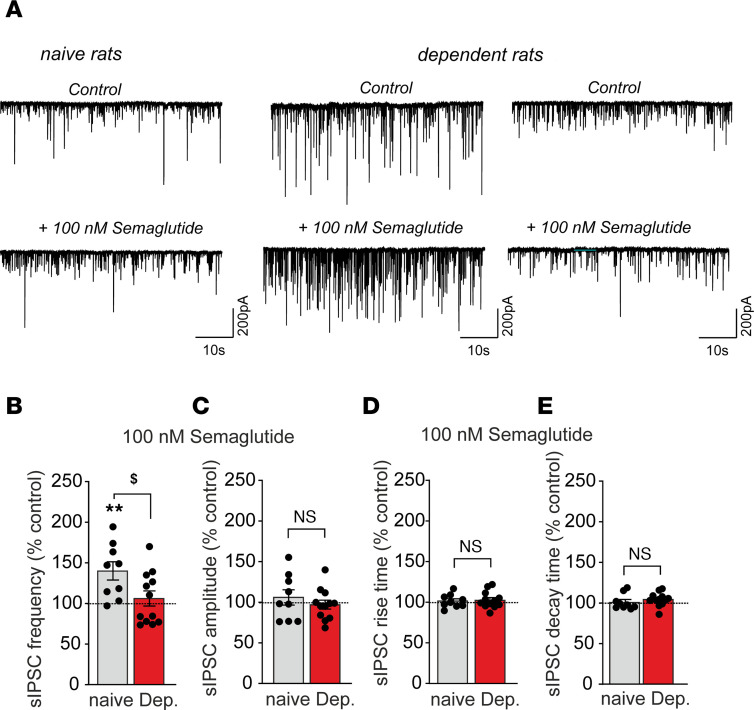
Figure 5. Semaglutide increased GABA transmission in pyramidal neurons in layer 5 of the infralimbic cortex (ILC) from alcohol-naive rats but had mixed effects in alcohol-dependent rats.
(A) Representative spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSC) traces during baseline control (upper panel) conditions and during superfusion of 100 nM semaglutide (lower panel). (B–E) Bar charts summarize the effects of semaglutide (100nM) on sIPSC frequencies (B), amplitudes (C), rise times (D), and decay times (E) from 9 to 12 neurons from alcohol-naive (gray bars) and alcohol-dependent rats (red bars). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Differences between semaglutide and baseline control conditions (dashed lines) were analyzed using 1-sample Student’s t tests (**P < 0.01). Differences of semaglutide effects on selected parameters between alcohol-naive and alcohol-dependent rats were calculated using unpaired Student’s t tests ($P < 0.05). Data were generated from 5 alcohol-naive and 7 alcohol-dependent rats, from 2 separate chronic, intermittent, alcohol vapor exposure cohorts.