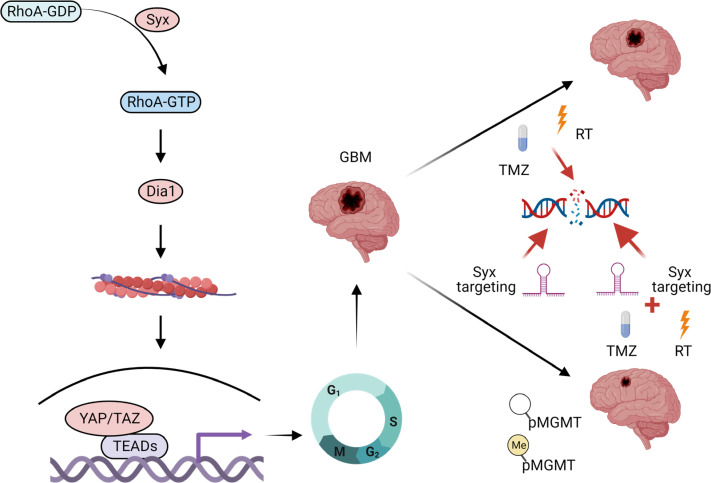
Figure 8. Schematic diagram of the Syx-RhoA-Dia1-YAP/TAZ signaling axis in cell cycle progression, DNA damage, and therapy resistance in GBM.
The RhoA GEF Syx activates RhoA and its downstream effector Dia1. This results in increased YAP/TAZ stability, nuclear translocation, and transactivation activity. The pathway contributes to cell cycle gene regulation, promoting GBM cell cycle progression and increased tumor growth. Syx targeting, like TMZ and radiation therapy (RT), promotes DNA double-strand breaks and potentiates GBM response to these treatments. This approach is independent of the MGMT promoter methylation status, presenting a potential therapeutic strategy for GBM.