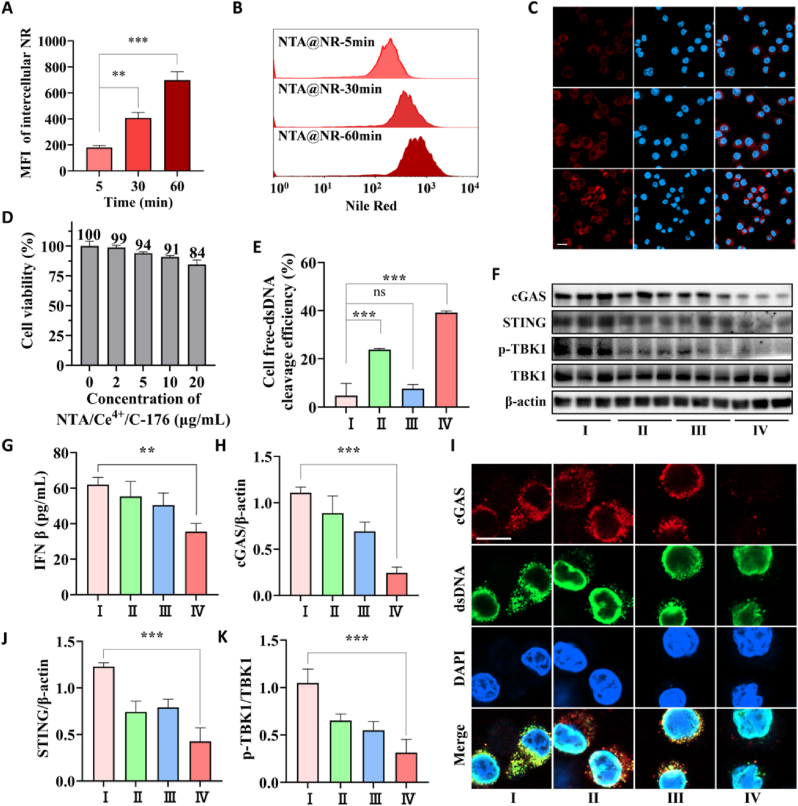
Fig. 3.
Biocompatibility and catalytic activity of NTA/Ce4+/C-176 in vitro. (A) Quantified NTA/Ce4+/Nile red cellular uptake in BV2 cells by flow cytometry analysis with increasing co-incubation time (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (B) Typical flow cytometry data of cellular uptake of NTA/Ce4+/Nile red in BV2 cells. (C) Confocal images of intracellular NTA/Ce4+/Nile red in BV2 cells. NTA/Ce4+/Nile red indicated by a red signal and nuclei stained by DAPI indicated by a blue signal; scale bar = 20 μm. (D) Viability of BV2 cells treated for 24 h with various concentrations of NTA/Ce4+/C-176 (n = 3). (E) Cell-free dsDNA cleavage efficiency of the pico-green-stained BV2-cultured supernatant. Data are means ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments; ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison tests, ns means no significant difference). (F) Representative immunoblotting of cGAS, STING, p-TBK1, and TBK1 in BV2 after indicated treatments (n = 3), using β-Actin as control. ELISA of (G) IFNβ, blotting quantification of (H) cGAS, (J) STING, and (K) p-TBK1. (I) Cellular immunofluorescence images of dsDNA (green) and cGAS (red) in BV2 cells. Scar bar = 10 μm.