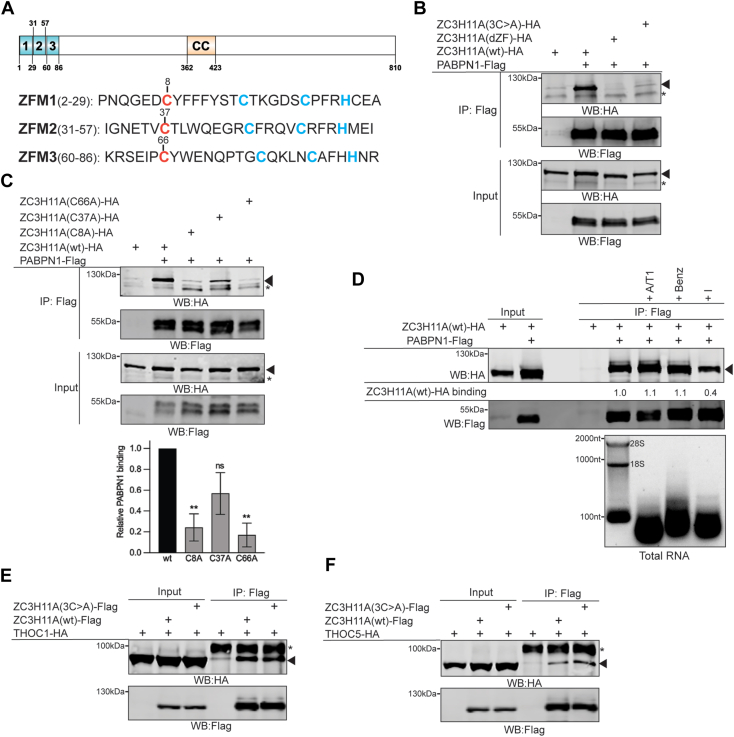
Figure 3.
Zinc finger motifs control ZC3H11A binding to PABPN1.A, a schematic drawing of the human ZC3H11A protein. Individual zinc finger motifs (ZFM1-3) and coil-coiled domain (CC) are indicated based on the uniport.org (O75152) annotation. Individual CCCH motifs are shown (red and blue). Mutated cysteine (Cys(C) to Ala(A)) is indicated in red. B, co-IP of the HA-tagged ZC3H11A proteins using PABPN1-Flag as the bait in transfected HEK293T cells. The 3C>A mutant includes C8A, C37A, and C66A triple mutations, whereas the dZF mutant lacks the entire N-terminus of the protein. Western blot (WB) analysis with the anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. An asterisk indicates an unspecific protein; arrowheads indicate migration of the ZC3H11A protein. C, co-IP of the individual ZC3H11A ZFM mutants with the PABPN1-Flag protein as the bait. After normalization to input, the relative binding of the individual ZFM mutants to PABPN1 is shown below the image (ZC3H11A(wt) = 1). Data (mean ± SEM, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01) from three individual experiments. D, co-IP of ZC3H11A(wt)-HA with PABPN1-Flag as a bait in the RNase A/T1 (+A/T1), benzonase (+Benz) or RNase I (+I) treated cell lysates. Quantification of ZC3H11A(wt)-HA binding is shown below the anti-HA blot, ZC3H11A(wt)-HA interaction with PABPN1-Flag in non-treated cell lysates was considered 1. The efficiency of the nuclease treatments in the cell lysates is shown on an agarose gel image below the protein images. Migration of 28S and 18S rRNA and DNA molecular weight markers are indicated. E, co-IP of THOC1-HA with either ZC3H11A(wt)-Flag or ZC3H11A(3C>A)-Flag as the baits. F, co-IP of THOC5-HA with either ZC3H11A(wt)-Flag or ZC3H11A(3C>A)-Flag as the baits. An asterisk indicates an unspecific protein, whereas the arrowheads indicate migration of the THOC1-HA and THOC5-HA proteins.