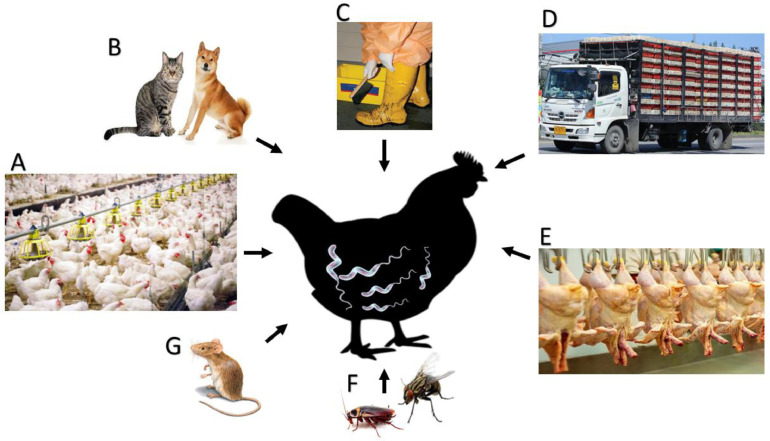
Figure 3.
The mechanisms of Campylobacter transmission in chickens. (A) Contaminated feed, water, and utensils at the farm level. (B) Carnivorous, especially dogs and cats. (C) Human movement between different farms with contaminated utensils. (D) During birds’ transportation from previously contaminated cages or contaminated environments. (E) At slaughterhouses level during bird evisceration and processing with previously contaminated machines. (F) Insects and (G) rodents (insects and rodents can transmit infection during all stages of bird rearing, transportation, slaughtering, processing, and handling).