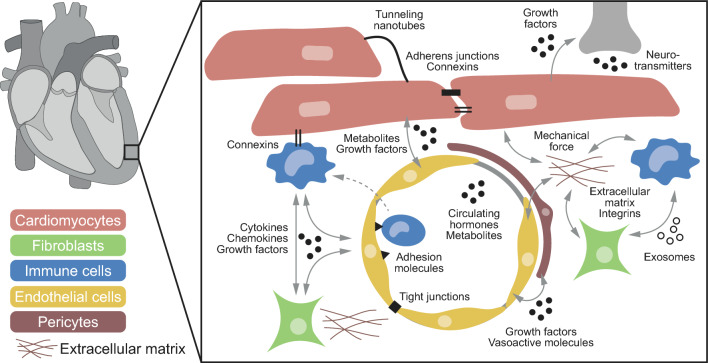
Fig. 2.
Heterocellular interactions in the healthy heart. Cell communication in the heart involves ‘biochemical’ and ‘biophysical’ cues. Secreted factors that act in a paracrine or autocrine manner include cytokines, chemokines, or growth factors. These factors may be secreted to the extracellular space, ‘wrapped up’ in exosomes, be transported via tunnelling nanotubes, etc. In addition, metabolites may act as signalling molecules. Cardiac cells are responsive to endocrine factors and neurotransmitters that may derive from the circulation or intracardiac nerve endings. Biophysical interactions involve direct mechanical cell–cell coupling via adherens junctions or tight junctions, as well as indirect mechanical coupling such as via extracellular matrix/integrins connections. Electrical coupling in the heart typically involves connexins, a class of transmembrane proteins that forms gap junctions between cells