Fig. 5.
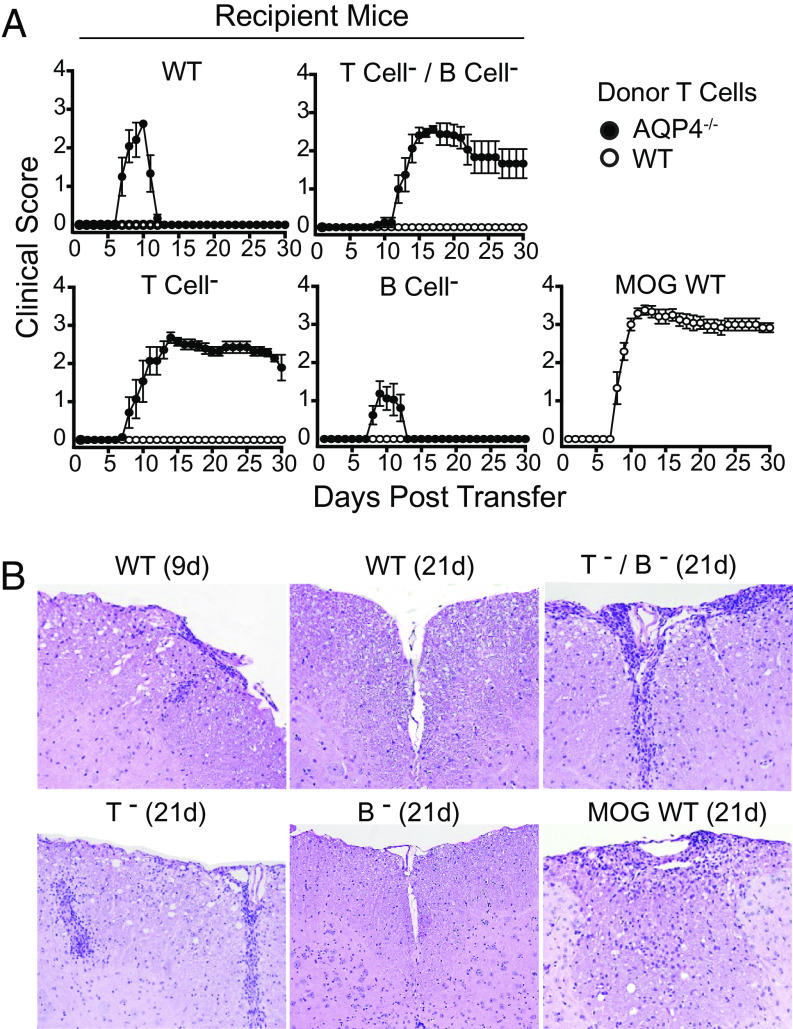
Pathogenic AQP4-specific Th17 cells induce sustained CNS autoimmune disease in T cell–deficient mice. (A) Th17-polarized AQP4 p133–149-specific T cells from AQP4−/− mice were transferred into WT, T cell– and B cell–deficient (T cell-/B cell-, RAG1−/−), T cell–deficient (T cell-, TCRα−/−) and B cell–deficient (B cell-, JHT) recipient mice then scored for clinical disease. Donor Th17-polarized MOG p35-55-specific T cells were transferred into WT recipient mice as a control. Results are representative of four experiments (n = 5 per group). (B) Recipient mice were evaluated for histologic evidence of meningeal and CNS parenchymal inflammation (H&E). Results are representative of two experiments (two to four mice/group/timepoint/experiment).