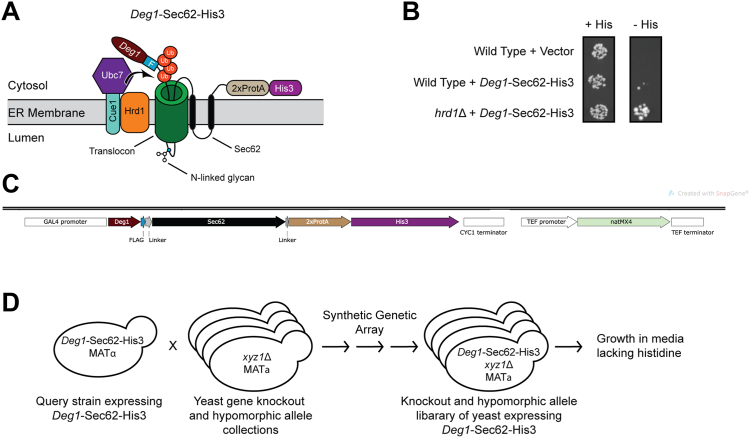
Figure 1.
Screen for genes required for degradation of a model translocon-associated protein.A, schematic of Deg1-Sec62-His3 following aberrant translocon engagement. Following the integration of the two transmembrane segments of Sec62, the N-terminal tail of the fusion protein loops into and persistently engages (i.e., clogs) the translocon (14). Upon clogging, Deg1-Sec62(±His3) undergoes N-linked glycosylation and is ubiquitylated by Hrd1 and Ubc7 (which is anchored at the ER membrane by Cue1). Deg1-Sec62-His3 possesses, in sequence, Deg1 (the N-terminal 67 amino acids from the yeast transcriptional repressor MATα2), a FLAG epitope (F), Sec62, two copies of Staphylococcus aureus Protein A (2xProtA), and the His3 enzyme. Ub, ubiquitin. B, yeast of the indicated genotypes transformed with an empty vector or a plasmid encoding Deg1-Sec62-His3 were spotted onto media containing or lacking histidine (His). C, DOA10 locus of the query strain used for the genome-wide screen. DOA10 was replaced with a cassette containing Deg1-Sec62-His3 and natMX4 as two independent genes, each with its own promoter and transcriptional terminator. D, overview of the genome-wide screen. See text and Table 1 for details.